Gdy letnie upały sięgają zenitu, sprawny klimatyzator to nie tylko luksus - to konieczność. Ale co się dzieje, gdy zaufany klimatyzator nagle zaczyna wydmuchiwać ciepłe powietrze? Niniejszy kompleksowy przewodnik przedstawia przyczyny tego powszechnego problemu, dostarczając zarówno prostych wyjaśnień dla właścicieli domów, jak i dogłębnych informacji technicznych dla specjalistów HVAC.
Brudny filtr powietrza: Powszechny winowajca
Jedną z najczęstszych przyczyn słabej wydajności klimatyzacji jest zanieczyszczony filtr powietrza. Aby to zrozumieć, wyobraź sobie, że próbujesz oddychać przez zatkaną słomkę. Z trudem, prawda? Podobnie zabrudzony filtr powietrza ogranicza przepływ powietrza, utrudniając klimatyzacji skuteczne chłodzenie domu.
Zmniejszony przepływ powietrza ma kilka konsekwencji. Po pierwsze, zmniejsza wydajność chłodzenia systemu. Po drugie, zmusza klimatyzację do cięższej pracy, co prowadzi do zwiększonego zużycia energii. I wreszcie, może nawet spowodować zamarznięcie wężownicy parownika, problem, który omówimy bardziej szczegółowo później.
Jak często należy wymieniać filtr AC?
Na częstotliwość wymiany filtrów wpływa kilka czynników. Należą do nich częstotliwość korzystania z klimatyzacji, typ posiadanego filtra oraz obecność zwierząt domowych lub alergików w gospodarstwie domowym. Ogólną zasadą jest sprawdzanie filtra co miesiąc.
Jeśli często korzystasz z klimatyzacji lub masz problemy z alergią, może być konieczna częstsza wymiana filtra. W przypadku większości gospodarstw domowych wymiana filtra co jeden do trzech miesięcy jest wystarczająca.
Rodzaje filtrów AC
Rynek oferuje różne typy filtrów AC, z których każdy ma swoje zalety i wady. Filtry z włókna szklanego są najbardziej podstawową i niedrogą opcją, ale są również najmniej skuteczne w zatrzymywaniu małych cząstek. Filtry plisowane stanowią krok naprzód, zapewniając dobrą równowagę między kosztem a skutecznością, zatrzymując więcej kurzu, pyłków i innych cząstek unoszących się w powietrzu. Dla osób z alergiami lub wrażliwością układu oddechowego najlepszym wyborem są filtry HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air), oferujące najwyższy poziom filtracji, choć mają wyższą cenę. Wreszcie, filtry wielokrotnego użytku stanowią opcję przyjazną dla środowiska, ponieważ można je myć i używać ponownie. Wymagają one jednak regularnego czyszczenia, aby zachować swoją skuteczność.
Zamarznięte cewki parownika: Przyczyny i rozwiązania
Zamarznięte wężownice parownika są kolejnym częstym winowajcą nieprawidłowego chłodzenia klimatyzacji. Dzieje się tak często z powodu ograniczonego przepływu powietrza, jak omówiliśmy w przypadku zabrudzonych filtrów lub niskiego poziomu czynnika chłodniczego.
Gdy przepływ powietrza jest ograniczony, czynnik chłodniczy wewnątrz wężownic staje się zbyt zimny. Powoduje to, że wilgoć z otaczającego powietrza skrapla się i zamarza na wężownicach. Rezultat? Zmniejszone chłodzenie, a w ciężkich przypadkach potencjalne uszkodzenie sprężarki klimatyzacji, serca systemu.
Oznaki zamarzniętych cewek parownika
Podejrzenie zamarzniętych wężownic parownika można wysunąć w przypadku zaobserwowania widocznego lodu tworzącego się na samych wężownicach lub na przewodach czynnika chłodniczego. Ponadto silnym wskaźnikiem jest zauważalny spadek przepływu powietrza z otworów wentylacyjnych. W miarę topnienia lodu mogą również wystąpić wycieki wody z klimatyzatora. Wreszcie, nietypowe dźwięki, takie jak syczenie lub bulgotanie, mogą sygnalizować problem z wężownicami.
Niski poziom czynnika chłodniczego i zamarznięte wężownice
Niski poziom czynnika chłodniczego może również powodować zamarzanie wężownic parownika. Czynnik chłodniczy to substancja, która pochłania ciepło z powietrza w pomieszczeniu. Gdy ilość czynnika chłodniczego jest niewystarczająca, pochłania on mniej ciepła, co prowadzi do znacznego spadku temperatury wężownicy i potencjalnego zamarzania.
Taka sytuacja może również obciążyć sprężarkę. Sprężarka jest zaprojektowana do pracy z określoną ilością czynnika chłodniczego. Gdy jego poziom jest niski, może dojść do przegrzania i potencjalnej awarii.
Wycieki czynnika chłodniczego: Poważny problem
Wycieki czynnika chłodniczego to poważny problem, który może znacząco wpłynąć na wydajność klimatyzacji i zaszkodzić środowisku. Czynnik chłodniczy ma kluczowe znaczenie dla procesu chłodzenia; pochłania ciepło z powietrza w pomieszczeniu i uwalnia je na zewnątrz.
Nieszczelności nie tylko zmniejszają wydajność chłodzenia klimatyzacji, ale także prowadzą do zwiększonego zużycia energii, ponieważ system pracuje ciężej, aby to zrekompensować. Ponadto mogą one spowodować uszkodzenie sprężarki i stanowić zagrożenie dla środowiska.
Rodzaje czynników chłodniczych
Rodzaj czynnika chłodniczego stosowanego w systemach klimatyzacji ewoluował w czasie. R-22 (Freon), starszy czynnik chłodniczy, jest wycofywany ze względu na jego potencjał niszczenia warstwy ozonowej. R-410A (Puron) został wprowadzony jako bardziej przyjazny dla środowiska zamiennik. Obecnie inne czynniki chłodnicze, takie jak R-32 i R-454B, pojawiają się jako alternatywy o jeszcze niższym potencjale globalnego ocieplenia.
Jak wykrywać wycieki czynnika chłodniczego
Do wykrywania wycieków czynnika chłodniczego można wykorzystać kilka metod. Elektroniczne wykrywacze nieszczelności to specjalistyczne urządzenia zaprojektowane do wykrywania obecności czynnika chłodniczego. Inna technika polega na dodaniu barwnika UV do systemu; jeśli istnieje wyciek, barwnik będzie świecił w świetle UV, dzięki czemu wyciek będzie łatwy do wykrycia. Prosty test bąbelkowy można również wykonać, nakładając roztwór mydła na podejrzane obszary wycieku - bąbelki będą się tworzyć, jeśli czynnik chłodniczy ucieka. Wreszcie, test ciśnieniowy, który obejmuje monitorowanie ciśnienia w układzie, może ujawnić spadki wskazujące na wyciek.
Szukasz rozwiązań energooszczędnych aktywowanych ruchem?
Skontaktuj się z nami, aby uzyskać kompletne czujniki ruchu PIR, produkty energooszczędne aktywowane ruchem, przełączniki czujników ruchu i rozwiązania komercyjne w zakresie obecności/pobytu.
Zagrożenia dla zdrowia związane z wyciekami czynnika chłodniczego
Szybkie usuwanie wycieków czynnika chłodniczego ma kluczowe znaczenie nie tylko dla wydajności klimatyzacji, ale także ze względów zdrowotnych i środowiskowych. Wdychanie czynnika chłodniczego może prowadzić do zawrotów głowy, bólów głowy, nudności, a w ciężkich przypadkach do utraty przytomności. Bezpośredni kontakt ze skórą lub oczami może powodować podrażnienia, a nawet odmrożenia. Ponadto, wpływ wycieków czynnika chłodniczego na środowisko jest znaczący. Starsze czynniki chłodnicze przyczyniają się do niszczenia warstwy ozonowej, podczas gdy nowsze, choć mniej szkodliwe, nadal mają znaczny potencjał globalnego ocieplenia.
Problemy ze sprężarką: Serce klimatyzacji
Sprężarka jest sercem systemu klimatyzacji. Odpowiada za cyrkulację czynnika chłodniczego, który umożliwia proces chłodzenia. Zadaniem sprężarki jest sprężanie czynnika chłodniczego, co zwiększa jego temperaturę i ciśnienie. Jest to krytyczny etap w procesie wymiany ciepła, który ostatecznie chłodzi powietrze w domu.
Rodzaje sprężarek AC
W systemach klimatyzacji stosuje się kilka typów sprężarek, z których każdy ma swoją własną charakterystykę. Sprężarki tłokowe, powszechnie stosowane w starszych urządzeniach, wykorzystują tłoki do sprężania czynnika chłodniczego, podobnie jak silnik samochodowy. Sprężarki spiralne są generalnie bardziej wydajne i cichsze, wykorzystując dwie spirale w kształcie spirali do sprężania czynnika chłodniczego. Sprężarki rotacyjne, często spotykane w mniejszych jednostkach, są kompaktowe i wydajne, wykorzystując obracającą się łopatkę do sprężania. Sprężarki śrubowe są zwykle używane w dużych systemach komercyjnych ze względu na ich wysoką wydajność, wykorzystując dwie zazębiające się śruby do sprężania.
Oznaki awarii sprężarki
Awaria sprężarki często objawia się kilkoma znakami ostrzegawczymi. Możesz zauważyć zmniejszoną wydajność chłodzenia, a klimatyzacja nie chłodzi tak skutecznie, jak kiedyś. Nietypowe odgłosy, takie jak zgrzytanie, piszczenie lub brzęczenie również mogą wskazywać na problem. Jeśli sprężarka pobiera zbyt dużo mocy, może to spowodować zadziałanie wyłącznika automatycznego. Trudny rozruch, gdy sprężarka ma trudności z uruchomieniem, to kolejny sygnał ostrzegawczy. Wreszcie, zwiększone zużycie energii i wyższe rachunki mogą wskazywać na to, że sprężarka pracuje ciężej niż powinna.
Długoterminowe skutki działania klimatyzacji z uszkodzoną sprężarką
Zignorowanie wadliwej sprężarki może mieć poważne konsekwencje. Dalsza eksploatacja może doprowadzić do dalszego uszkodzenia sprężarki, potencjalnie powodując jej całkowitą awarię. Dodatkowe obciążenie może również uszkodzić inne komponenty w systemie, prowadząc do efektu domina awarii. W najgorszym przypadku może dojść do awarii całego układu klimatyzacji. Nieprawidłowo działająca sprężarka prowadzi również do zwiększonych kosztów energii, ponieważ ma trudności z działaniem. Ostatecznie eksploatacja wadliwej sprężarki znacznie skróci żywotność klimatyzatora.
Problemy z termostatem: Czy klimatyzacja otrzymuje właściwe sygnały?
Termostat jest mózgiem systemu klimatyzacji. Odpowiada za sterowanie pracą urządzenia, włączając je i wyłączając w zależności od żądanej temperatury. Wyczuwa on temperaturę w pomieszczeniu i sygnalizuje jednostce klimatyzacyjnej, aby odpowiednio rozpoczęła lub zakończyła chłodzenie.
Rodzaje termostatów
Podobnie jak sprężarki, termostaty ewoluowały z czasem. Termostaty elektromechaniczne, starszego typu, wykorzystują pasek bimetaliczny do wykrywania zmian temperatury i są generalnie mniej dokładne niż nowsze modele. Termostaty cyfrowe oferują większą dokładność i często są wyposażone w programowalne funkcje, pozwalające zaplanować różne temperatury dla różnych pór dnia. Inteligentne termostaty stanowią najnowsze osiągnięcie, oferując łączność Wi-Fi do zdalnego sterowania, możliwości uczenia się w celu dostosowania do preferencji użytkownika oraz potencjał optymalizacji zużycia energii. Oferują one potencjalne długoterminowe oszczędności energii, ale mogą również budzić obawy o prywatność i mają bardziej stromą krzywą uczenia się.
Jak przetestować termostat
Najpierw sprawdź wyświetlacz, aby upewnić się, że jest włączony i wyświetla prawidłowe ustawienia. Następnie spróbuj zmienić ustawienie temperatury. Ustaw ją o kilka stopni niżej niż aktualna temperatura w pomieszczeniu i poczekaj, aż włączy się klimatyzacja.
Jeśli wyświetlacz jest pusty, konieczna może być wymiana baterii. Jeśli to nie zadziała, możesz sprawdzić okablowanie pod kątem luźnych lub uszkodzonych połączeń. Jeśli jednak nie czujesz się komfortowo podczas pracy z komponentami elektrycznymi, najlepiej skonsultować się z profesjonalistą. W niektórych przypadkach można tymczasowo ominąć termostat, aby sprawdzić, czy klimatyzacja się włączy, ale ponownie najlepiej pozostawić to wykwalifikowanemu technikowi.
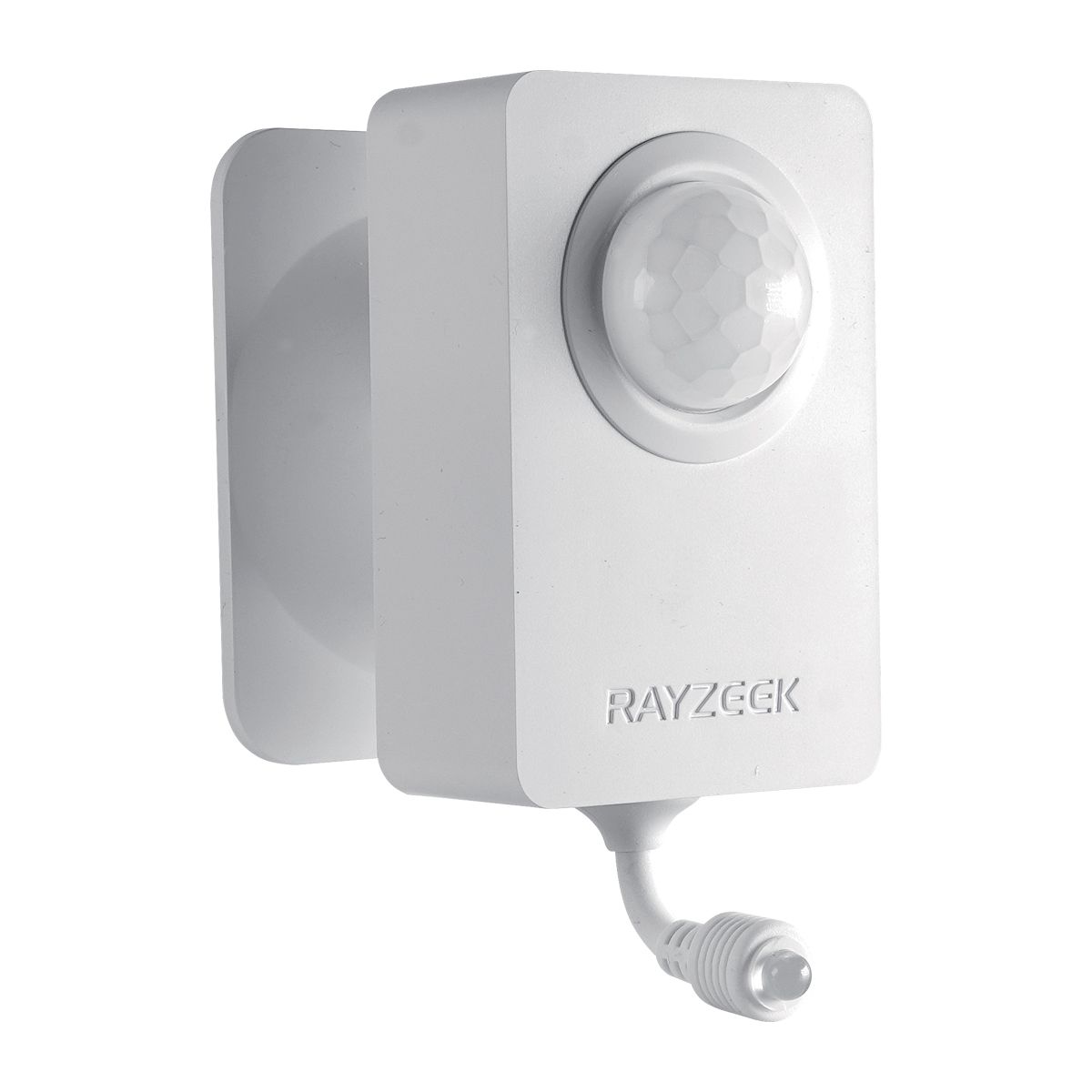
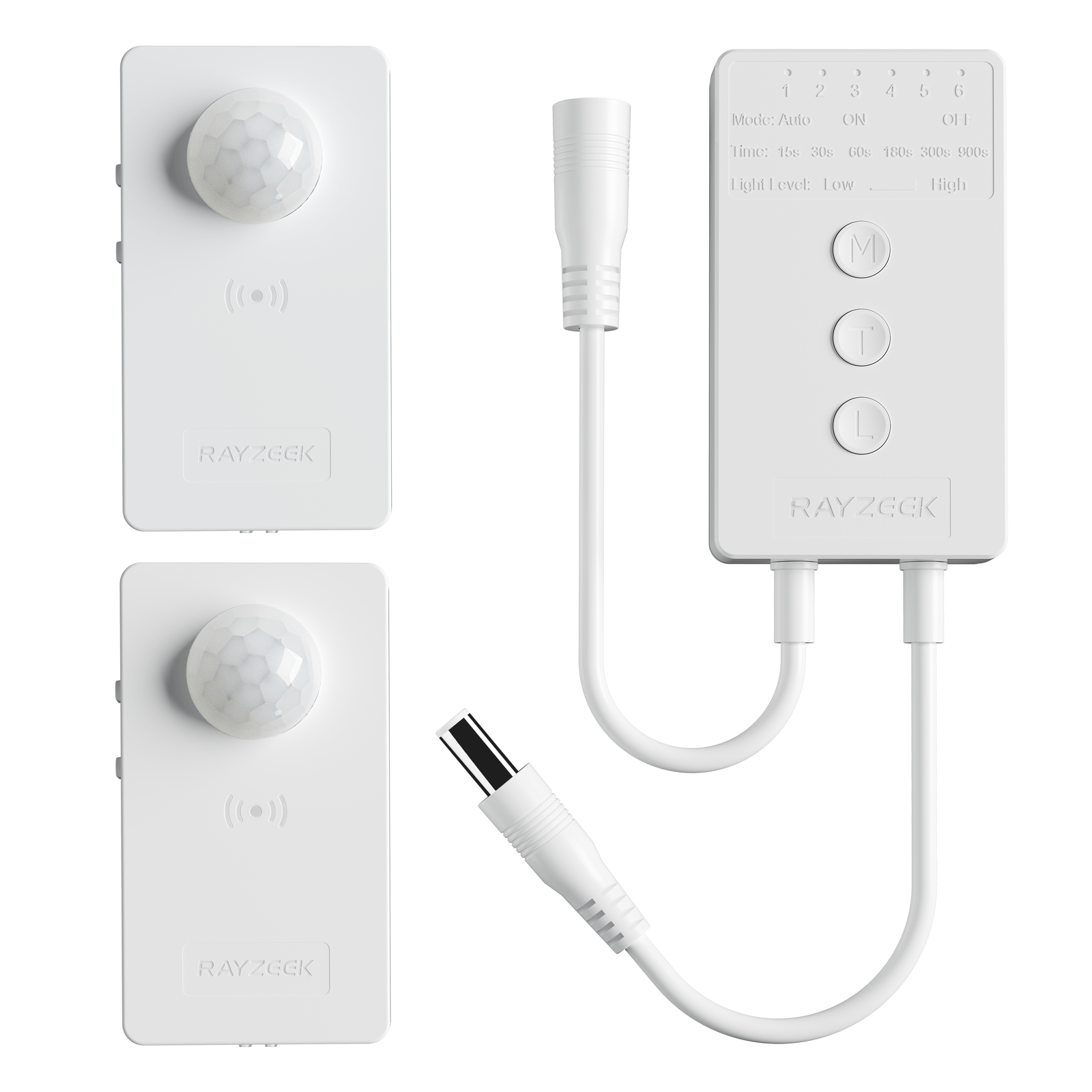
Chociaż termostaty są niezbędne do kontroli temperatury, mają one istotne ograniczenie: nie wiedzą, czy pomieszczenie jest rzeczywiście zajęte. Oznacza to, że klimatyzacja może pracować godzinami, chłodząc pustą przestrzeń i marnując energię. Jest to miejsce, w którym inteligentne rozwiązanie, takie jak Czujnik ruchu klimatyzatora RZ050 wkracza do akcji. To innowacyjne urządzenie automatycznie wyłącza klimatyzację, gdy opuszczasz pomieszczenie, dzięki czemu nie płacisz za chłodzenie pustej przestrzeni.
Czujnik ruchu klimatyzatora RZ050
Nigdy więcej nie zapomnij wyłączyć klimatyzacji
- Automatycznie wyłącza klimatyzację, gdy wychodzisz.
- Oszczędzaj energię i pieniądze bez wysiłku.
- Łatwy w instalacji i obsłudze, nie wymaga profesjonalnej pomocy.
Dzięki inteligentnemu wykrywaniu obecności, RZ050 dodaje warstwę automatyzacji, której brakuje nawet najbardziej zaawansowanym termostatom. To prosty, ale skuteczny sposób na zwiększenie wydajności klimatyzacji i przyczynienie się do bardziej zrównoważonego stylu życia.
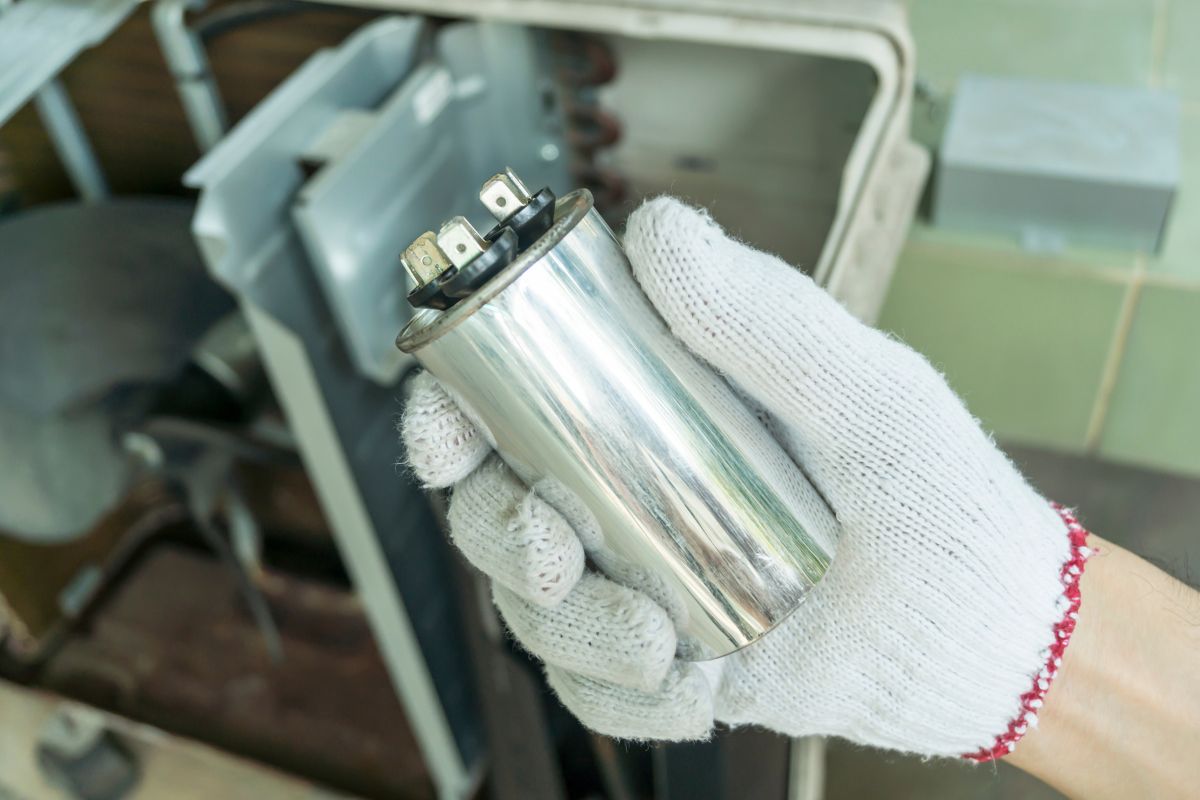
Problemy z kondensatorem: Problemy z uruchamianiem i działaniem
Kondensatory są niezbędnymi komponentami elektrycznymi, które zapewniają niezbędny impuls do uruchomienia i pracy silnika AC. Ich działanie polega na magazynowaniu i uwalnianiu energii elektrycznej, zapewniając silnikowi moc potrzebną do działania.
Jaka jest różnica między kondensatorem rozruchu i pracy?
Kondensator rozruchowy zapewnia dużą początkową dawkę energii potrzebną do uruchomienia silnika. Można to porównać do początkowego impulsu potrzebnego do rozpędzenia roweru. Z drugiej strony, kondensator rozruchowy zapewnia ciągły, mniejszy impuls, aby utrzymać płynną pracę silnika po jego uruchomieniu. Niektóre jednostki AC wykorzystują podwójny kondensator, który łączy funkcje rozruchu i pracy w jednym urządzeniu.
Diagnozowanie problemów z kondensatorem
Problemy z kondensatorami można często zidentyfikować za pomocą kombinacji metod. Kontrola wzrokowa może ujawnić fizyczne oznaki uszkodzenia, takie jak wybrzuszenie lub wyciek. Do bardziej technicznej oceny można użyć multimetru, aby zmierzyć pojemność kondensatora i porównać ją z wartością znamionową. Kilka objawów może również wskazywać na uszkodzony kondensator: jednostka AC może w ogóle się nie uruchamiać, może wydawać buczący dźwięk, może działać z przerwami lub może wystąpić słaby przepływ powietrza.
Może jesteś zainteresowany
Problemy z cewką skraplacza: Problemy z wymianą ciepła
Wężownice skraplacza odgrywają kluczową rolę w procesie chłodzenia. Są one odpowiedzialne za uwalnianie ciepła pochłoniętego przez czynnik chłodniczy do powietrza zewnętrznego. Zasadniczo ułatwiają one transfer ciepła z czynnika chłodniczego do środowiska zewnętrznego, umożliwiając schłodzenie czynnika chłodniczego i kontynuowanie cyklu.
Jak czyścić cewki skraplacza
Po pierwsze i najważniejsze, należy wyłączyć zasilanie klimatyzatora za pomocą wyłącznika automatycznego. Bezpieczeństwo przede wszystkim! Następnie użyj miękkiej szczotki lub odkurzacza, aby usunąć wszelkie luźne zanieczyszczenia, takie jak liście, brud lub ścinki trawy, które mogą blokować cewki.
Następnie można użyć węża ogrodowego z dyszą rozpylającą, aby delikatnie wyczyścić cewki. Alternatywnie można użyć komercyjnego środka do czyszczenia wężownic zaprojektowanego specjalnie do tego celu. Jeśli zauważysz wygięte żebra na wężownicach, ostrożnie wyprostuj je za pomocą grzebienia. Wygięte lamele mogą ograniczać przepływ powietrza i zmniejszać wydajność.
Konstrukcja wężownicy skraplacza i wydajność wymiany ciepła
Konstrukcja wężownic skraplacza znacząco wpływa na ich zdolność do przenoszenia ciepła. Ważną rolę odgrywają takie czynniki jak gęstość lameli. Większa gęstość żeber oznacza większą powierzchnię wymiany ciepła, co generalnie prowadzi do lepszej wydajności.
Materiał, z którego wykonane są cewki, również ma znaczenie. Powszechnie stosowane są miedź i aluminium, z których każdy ma inne właściwości wymiany ciepła. Ponadto konfiguracja wężownic, w tym ich kształt i rozmieszczenie, wpływa na przepływ powietrza i ogólną wydajność wymiany ciepła.
Problemy z kanałami wentylacyjnymi: Wycieki i zatory
Kanały wentylacyjne to system kanałów rozprowadzających schłodzone powietrze w całym domu. To jak układ krążenia w domu, dostarczający klimatyzowane powietrze do każdego pomieszczenia. Jednak problemy z przewodami, takie jak nieszczelności, zatory lub słaba izolacja, mogą znacząco wpłynąć na wydajność klimatyzacji.
Jak sprawdzić przewody wentylacyjne
Zacznij od sprawdzenia widocznych uszkodzeń przewodów wentylacyjnych. Mogą to być dziury, rozdarcia lub sekcje, które zostały odłączone. Następnie spróbuj wyczuć wycieki powietrza. Przytrzymaj dłoń w pobliżu połączeń i szwów kanałów, aby wykryć uciekające powietrze.
Słuchaj wszelkich nietypowych dźwięków, takich jak gwizdy lub dudnienie, które mogą wskazywać na wycieki lub zatory. Na koniec zwróć uwagę na temperaturę w różnych pomieszczeniach. Jeśli niektóre pomieszczenia są stale zbyt gorące lub zbyt zimne, może to być oznaką problemów z przewodami wentylacyjnymi.
Najlepsze praktyki uszczelniania i izolowania kanałów wentylacyjnych
Jeśli znajdziesz nieszczelności, ważne jest, aby je odpowiednio uszczelnić. W tym celu użyj uszczelniacza mastyksowego lub taśmy metalowej. Zwykła taśma klejąca nie jest odpowiednim rozwiązaniem, ponieważ z czasem ulega degradacji.
Jeśli kanały wentylacyjne przebiegają przez nieklimatyzowane przestrzenie, takie jak strychy lub puste przestrzenie, należy upewnić się, że są one odpowiednio zaizolowane. Powszechnym wyborem do tego celu jest izolacja z włókna szklanego z folią. Wreszcie, upewnij się, że wewnątrz kanałów nie ma żadnych przeszkód, które mogłyby ograniczać przepływ powietrza.
Zainspiruj się portfolio czujników ruchu Rayzeek.
Nie znalazłeś tego, czego szukasz? Nie martw się. Zawsze istnieją alternatywne sposoby rozwiązania problemów. Być może pomoże w tym jeden z naszych portfeli.
Problemy elektryczne: Problemy z zasilaniem
Problemy elektryczne mogą uniemożliwić jednostce klimatyzacyjnej otrzymanie zasilania potrzebnego do prawidłowego działania. Problemy te mogą obejmować zarówno proste wyłączniki, jak i bardziej złożone awarie okablowania lub komponentów. Typowe usterki elektryczne w systemach klimatyzacji obejmują zadziałanie wyłączników automatycznych lub przepalenie bezpieczników, które często są pierwszymi elementami do sprawdzenia. Luźne lub uszkodzone okablowanie może zakłócać przepływ energii elektrycznej, a wadliwe styczniki lub przekaźniki, które kontrolują przepływ energii elektrycznej do różnych części, również mogą być winowajcą. Ponadto sam silnik może mieć problemy z elektrycznością.
Środki ostrożności przy rozwiązywaniu problemów elektrycznych
- Wyłącz zasilanie: Przed przystąpieniem do jakichkolwiek prac przy podzespołach elektrycznych należy zawsze wyłączyć zasilanie klimatyzatora za pomocą wyłącznika automatycznego.
- Używaj izolowanych narzędzi: Pomoże to chronić przed porażeniem prądem.
- Noś buty z gumową podeszwą: Zapewnia to dodatkową warstwę izolacji.
- Unikaj mokrych warunków: Woda i elektryczność nie mieszają się.
- Wezwij profesjonalistę: Jeśli nie czujesz się komfortowo podczas pracy z elektrycznością, nie wahaj się wezwać wykwalifikowanego elektryka.
Konserwacja i profesjonalne naprawy
Regularna konserwacja ma kluczowe znaczenie dla utrzymania sprawnego działania systemu klimatyzacji. Może ona zapobiec problemom, poprawić wydajność i wydłużyć żywotność urządzenia. Kompleksowa konserwacja klimatyzacji zazwyczaj obejmuje czyszczenie lub wymianę filtrów powietrza, czyszczenie skraplacza i parownika, sprawdzanie poziomu czynnika chłodniczego, sprawdzanie połączeń elektrycznych, smarowanie ruchomych części, testowanie termostatu i sprawdzanie kanałów wentylacyjnych.
Wybór odpowiedniego technika HVAC
Wybierając technika HVAC, ważne jest, aby przeprowadzić badania. Sprawdź, czy posiada odpowiednią licencję i ubezpieczenie. Przeczytaj recenzje online i poproś o rekomendacje od znajomych lub rodziny.
Uzyskaj wiele ofert, aby porównać ceny i usługi. Zapytaj o doświadczenie technika i wszelkie istotne certyfikaty. Wreszcie, zapytaj o gwarancje i rękojmie na ich pracę.
Zrozumienie ocen SEER: Efektywność energetyczna i chłodzenie
SEER, czyli sezonowy współczynnik efektywności energetycznej, jest miarą wydajności chłodzenia klimatyzatora. Jest on obliczany poprzez podzielenie mocy chłodniczej w BTU (British Thermal Units) przez pobór energii w watogodzinach w typowym sezonie chłodniczym.
Jaki współczynnik SEER powinienem wybrać?
Wyższe oceny SEER wskazują na większą efektywność energetyczną. W większości regionów minimalna ocena SEER dla nowych jednostek AC wynosi 13 lub 14. Jednak w cieplejszym klimacie może być wymagana wyższa ocena.
Wybierając współczynnik SEER, należy wziąć pod uwagę klimat, budżet i długoterminowe oszczędności. Jednostki o wyższym współczynniku SEER są droższe z góry, ale z czasem mogą zaoszczędzić pieniądze na rachunkach za energię.
Oceny SEER i długoterminowe oszczędności kosztów
Podczas gdy jednostki o wyższym współczynniku SEER mają wyższy koszt początkowy, mogą one prowadzić do znacznych oszczędności na rachunkach za energię w całym okresie ich eksploatacji. Aby określić potencjalny zwrot z inwestycji, można obliczyć okres zwrotu. Oszacuj roczne oszczędności energii uzyskane dzięki jednostce o wyższym współczynniku SEER i porównaj je z różnicą w kosztach początkowych.
Ważne jest, aby pamiętać, że SEER nie zawsze dokładnie odzwierciedla rzeczywiste zużycie energii we wszystkich klimatach. Inne wskaźniki, takie jak EER (współczynnik efektywności energetycznej) i HSPF (współczynnik sezonowej wydajności grzewczej), powinny być również brane pod uwagę w celu bardziej kompleksowego zrozumienia wydajności jednostki.
Żywotność klimatyzatora: Kiedy wymienić system
Średnia żywotność klimatyzatora wynosi około 15-20 lat przy odpowiedniej konserwacji. Jednakże, kilka czynników może mieć na to wpływ.
Oznaki, że nadszedł czas na nową jednostkę AC
Kilka wskaźników może sygnalizować, że nadszedł czas, aby rozważyć zakup nowego klimatyzatora. Częste awarie wymagające ciągłych napraw to poważny sygnał ostrzegawczy. Podobnie, zauważalny i niewyjaśniony wzrost rachunków za energię może sugerować, że klimatyzacja traci wydajność z powodu wieku. Niespójne chłodzenie, w którym klimatyzacja ma trudności z utrzymaniem komfortowej temperatury, to kolejny znak ostrzegawczy. Jeśli Twoja jednostka ma ponad 15 lat, dobrym pomysłem jest rozpoczęcie planowania wymiany. Wreszcie, jeśli urządzenie nadal wykorzystuje czynnik chłodniczy R-22, który jest stopniowo wycofywany, zaleca się modernizację do modelu bardziej przyjaznego dla środowiska.
Czynniki wpływające na żywotność jednostki AC
Na żywotność klimatyzatora może mieć wpływ kilka czynników. Regularna konserwacja ma kluczowe znaczenie dla wydłużenia jego żywotności. Wzorce użytkowania również odgrywają rolę; częstsze użytkowanie może prowadzić do krótszej żywotności. Kolejnym czynnikiem jest klimat, ponieważ ekstremalne temperatury mogą bardziej obciążać jednostkę. Jakość początkowej instalacji ma zasadnicze znaczenie dla optymalnej wydajności i długowieczności. Wreszcie, jakość samego oryginalnego sprzętu będzie naturalnie wpływać na jego żywotność.