W erze, w której efektywność energetyczna i spersonalizowany komfort stają się coraz ważniejsze, wiele osób ponownie rozważa opcje chłodzenia i ogrzewania domu. Czy kiedykolwiek zastanawiałeś się, czy istnieje bardziej wydajny sposób na chłodzenie domu niż poleganie na tradycyjnej centralnej klimatyzacji lub hałaśliwych jednostkach okiennych? Oto klimatyzator mini-split, bezkanałowy system, który szybko zyskuje na popularności. Niniejszy artykuł zawiera kompleksowy przegląd systemów mini-split, analizując ich komponenty, działanie, zalety, wady i porównania z innymi opcjami chłodzenia. Niezależnie od tego, czy jesteś po prostu ciekawy tej technologii, czy też jesteś doświadczonym badaczem poszukującym dogłębnych informacji, ten przewodnik zapewni Ci dogłębne zrozumienie klimatyzatorów mini-split.
Co to jest klimatyzator typu Mini Split?
Klimatyzator typu mini-split, znany również jako bezkanałowy mini-split, to rodzaj systemu ogrzewania i chłodzenia, który zapewnia klimatyzowane powietrze bez konieczności stosowania tradycyjnych kanałów. W przeciwieństwie do centralnych systemów klimatyzacji, które opierają się na sieci kanałów do rozprowadzania powietrza w całym budynku, mini-splity wykorzystują pojedyncze jednostki wewnętrzne połączone z zewnętrzną sprężarką/skraplaczem za pomocą przewodów czynnika chłodniczego.
Każda jednostka wewnętrzna jest odpowiedzialna za chłodzenie (lub ogrzewanie) określonej strefy lub obszaru. Pozwala to na niezależną kontrolę temperatury w różnych częściach budynku. Wyobraź sobie możliwość chłodzenia sypialni w nocy bez konieczności zamrażania reszty domu! Mini-splity oferują wydajną i elastyczną alternatywę dla tradycyjnych systemów HVAC, szczególnie w sytuacjach, w których instalacja przewodów jest niepraktyczna lub kosztowna, na przykład w starszych domach lub nowych dodatkach.
Rodzaje systemów mini split
Systemy mini-split występują w dwóch podstawowych konfiguracjach: jednostrefowej i wielostrefowej.
Jednostrefowe minisplity
Jednostrefowe systemy mini-split to najprostsza konfiguracja, składająca się z jednej jednostki wewnętrznej podłączonej do jednej jednostki zewnętrznej. Systemy te są przeznaczone do wydajnego chłodzenia lub ogrzewania pojedynczego pomieszczenia lub obszaru. Są idealnym rozwiązaniem dla mniejszych przestrzeni, dodatków do domu lub pomieszczeń, które nie są odpowiednio obsługiwane przez centralny system HVAC. Na przykład system jednostrefowy może być idealnym rozwiązaniem dla nowo wykończonej piwnicy, domowego biura lub solarium, które ma tendencję do zbytniego nagrzewania się latem.
Wielostrefowe minisplity
Wielostrefowe systemy mini-split idą o krok dalej, łącząc wiele jednostek wewnętrznych z jedną jednostką zewnętrzną. Taka konfiguracja pozwala na niezależne chłodzenie lub ogrzewanie wielu pomieszczeń lub stref, każda z własnym ustawieniem temperatury. Systemy wielostrefowe doskonale nadają się do większych domów lub budynków, w których różne obszary mają różne wymagania temperaturowe. Na przykład, można mieć jedną jednostkę chłodzącą salon, inną dla kuchni i oddzielne jednostki dla każdej sypialni, wszystkie podłączone do tej samej jednostki zewnętrznej. Oferując większą elastyczność i możliwość dostosowania, systemy wielostrefowe są zazwyczaj droższe niż systemy jednostrefowe.
Wybór odpowiedniego rozmiaru mini split
Prawidłowe dobranie rozmiaru ma kluczowe znaczenie dla optymalnej wydajności i efektywności systemu mini-split. Wydajność chłodnicza klimatyzatorów mierzona jest w brytyjskich jednostkach cieplnych (BTU). BTU to ilość ciepła wymagana do podniesienia temperatury jednego funta wody o jeden stopień Fahrenheita. Zgodnie z ogólną zasadą, potrzeba około 20 BTU na stopę kwadratową powierzchni mieszkalnej.
Na wymagany rozmiar może jednak wpływać kilka czynników:
- Wielkość pokoju (metraż kwadratowy): Większe pomieszczenia wymagają większej wydajności chłodzenia.
- Wysokość sufitu: Wyższe sufity zwiększają objętość chłodzonego powietrza.
- Jakość izolacji: Dobrze izolowane pomieszczenia lepiej zatrzymują chłodne powietrze, zmniejszając obciążenie chłodnicze.
- Liczba i rozmiar okien: Okna mogą przepuszczać znaczne ilości ciepła, zwłaszcza jeśli są skierowane na południe.
- Lokalny klimat: Gorętsze klimaty wymagają większej mocy chłodzenia.
- Urządzenia wytwarzające ciepło: Kuchnie i pomieszczenia z elektroniką mogą wymagać dodatkowego chłodzenia.
Ważne jest, aby unikać przewymiarowania lub niedowymiarowania systemu. Przewymiarowane jednostki mogą prowadzić do krótkich cykli, w których jednostka włącza się i wyłącza zbyt często. Zmniejsza to wydajność, skraca żywotność sprzętu i powoduje słabą kontrolę wilgotności. Z drugiej strony, niewymiarowe jednostki będą miały trudności z odpowiednim chłodzeniem przestrzeni, co prowadzi do dyskomfortu i zwiększonego zużycia energii.
Aby określić dokładną wymaganą wydajność chłodzenia, profesjonalni wykonawcy HVAC stosują obliczenia obciążenia Manual J. Ta kompleksowa ocena uwzględnia wszystkie wymienione powyżej czynniki, aby zapewnić idealne dopasowanie systemu do potrzeb domu.
Kluczowe komponenty systemu Mini Split
Aby zrozumieć, jak działa mini-split, warto poznać jego główne komponenty:
Jednostka wewnętrzna
Jednostka wewnętrzna, znana również jako centrala wentylacyjna lub parownik, to część systemu zamontowana wewnątrz pomieszczenia. Może być zainstalowana na ścianie, suficie lub podłodze, w zależności od modelu i preferencji użytkownika. Wewnątrz znajduje się wężownica parownika, filtr powietrza, wentylator i żaluzje kierunkowe.
Wężownica parownika to miejsce, w którym dzieje się magia. Pochłania ona ciepło z powietrza w pomieszczeniu, schładzając je. Następnie wentylator rozprowadza schłodzone powietrze po całym pomieszczeniu, podczas gdy filtr powietrza usuwa kurz, pyłki i inne unoszące się w powietrzu cząsteczki, poprawiając jakość powietrza w pomieszczeniu. Żaluzje można regulować, aby skierować przepływ powietrza w celu uzyskania optymalnego komfortu, zapewniając, że chłodne powietrze dotrze do każdego zakątka pomieszczenia.
Jednostka zewnętrzna
Jednostka zewnętrzna, znana również jako jednostka sprężarki/skraplacza, znajduje się na zewnątrz budynku, zazwyczaj na betonowym podłożu. Zawiera sprężarkę, wężownicę skraplacza i wentylator. Sprężarka jest sercem systemu, cyrkulującym czynnik chłodniczy pomiędzy jednostką wewnętrzną i zewnętrzną.
Zadaniem wężownicy skraplacza jest uwalnianie ciepła pochłanianego z powietrza w pomieszczeniu na zewnątrz. Wentylator pomaga rozproszyć to ciepło, zapewniając wydajną pracę systemu. Jednostka zewnętrzna została zaprojektowana tak, aby była odporna na warunki atmosferyczne i działała cicho, dzięki czemu nie przeszkadza w aktywności na świeżym powietrzu.
Przewody czynnika chłodniczego
Przewody czynnika chłodniczego to miedziane rurki, które łączą jednostkę wewnętrzną i zewnętrzną, tworząc zamkniętą pętlę, przez którą przepływa czynnik chłodniczy. Istnieją dwa główne przewody: przewód cieczowy i przewód ssawny. Przewód cieczowy transportuje ciekły czynnik chłodniczy pod wysokim ciśnieniem z jednostki zewnętrznej do jednostki wewnętrznej, natomiast przewód ssawny transportuje pary czynnika chłodniczego pod niskim ciśnieniem z powrotem do jednostki zewnętrznej.
Przewody te są izolowane, aby zapobiec stratom energii i zapewnić wydajną pracę systemu. Rodzaj używanego czynnika chłodniczego może się różnić, ale wiele nowoczesnych systemów wykorzystuje przyjazne dla środowiska opcje, takie jak R-410A.
Przewód spustowy kondensatu
Przewód odprowadzania skroplin to rura o małej średnicy, która odprowadza skropliny wytwarzane przez jednostkę wewnętrzną. Gdy wężownica parownika chłodzi powietrze, para wodna zawarta w powietrzu skrapla się do postaci ciekłej. Jest to podobne do tworzenia się kropelek wody na zewnętrznej stronie zimnej szklanki w upalny dzień.
Zainspiruj się portfolio czujników ruchu Rayzeek.
Nie znalazłeś tego, czego szukasz? Nie martw się. Zawsze istnieją alternatywne sposoby rozwiązania problemów. Być może pomoże w tym jeden z naszych portfeli.
Przewód odprowadzania skroplin odprowadza tę wodę na zewnątrz lub do odpływu, zapobiegając uszkodzeniom spowodowanym przez wodę i rozwojowi pleśni. Prawidłowe odprowadzanie skroplin jest niezbędne do utrzymania zdrowego środowiska wewnętrznego i zapewnienia długowieczności systemu.
Jak działa system Mini Split?
Mini-splity działają w oparciu o cykl chłodniczy, proces podobny do innych klimatyzatorów. Cykl ten obejmuje ciągłą cyrkulację czynnika chłodniczego między jednostką wewnętrzną i zewnętrzną, przenosząc ciepło z wnętrza na zewnątrz.
Tryb chłodzenia:
- Sprężarka w jednostce zewnętrznej spręża czynnik chłodniczy, zwiększając jego temperaturę i ciśnienie, zamieniając go w gorący gaz o wysokim ciśnieniu.
- Gorący czynnik chłodniczy przepływa do wężownicy skraplacza, gdzie uwalnia ciepło do powietrza zewnętrznego. Wentylator w jednostce zewnętrznej pomaga w rozpraszaniu ciepła.
- Gdy czynnik chłodniczy traci ciepło, skrapla się w ciecz pod wysokim ciśnieniem.
- Ciekły czynnik chłodniczy przepływa przez przewód cieczowy do jednostki wewnętrznej.
- W jednostce wewnętrznej czynnik chłodniczy przechodzi przez zawór rozprężny, który znacznie obniża jego ciśnienie i temperaturę.
- Teraz zimny czynnik chłodniczy o niskim ciśnieniu wpływa do wężownicy parownika.
- Ciepłe powietrze w pomieszczeniu jest wdmuchiwane przez wężownicę parownika. Czynnik chłodniczy pochłania ciepło z powietrza i odparowuje do postaci pary o niskim ciśnieniu.
- Schłodzone powietrze jest ponownie wprowadzane do pomieszczenia, obniżając temperaturę.
- Pary czynnika chłodniczego o niskim ciśnieniu powracają do jednostki zewnętrznej przez przewód ssawny.
- Cykl powtarza się w sposób ciągły, utrzymując żądaną temperaturę wewnętrzną.
Tryb ogrzewania (modele z pompą ciepła):
Wiele systemów mini-split to także pompy ciepła, co oznacza, że mogą one zapewniać zarówno chłodzenie, jak i ogrzewanie. W trybie ogrzewania proces jest zasadniczo odwracany za pomocą zaworu rewersyjnego.
- Jednostka wewnętrzna działa jak skraplacz, uwalniając ciepło do pomieszczenia.
- Jednostka zewnętrzna działa jak parownik, pochłaniając ciepło z powietrza zewnętrznego, nawet w niskich temperaturach.
Możliwość odwrócenia cyklu chłodzenia sprawia, że pompy ciepła typu mini-split są wszechstronnym i energooszczędnym rozwiązaniem zapewniającym komfort przez cały rok.
Technologia inwerterowa w minisplitach
Technologia inwerterowa jest kluczową cechą, która odróżnia wiele nowoczesnych systemów mini-split od tradycyjnych klimatyzatorów. Podczas gdy starsze klimatyzatory wykorzystują sprężarki o stałej prędkości, które włączają się i wyłączają, aby utrzymać żądaną temperaturę, mini-splity z inwerterem wykorzystują sprężarki o zmiennej prędkości. Ta pozornie niewielka różnica ma znaczący wpływ na wydajność i efektywność.
Technologia sprężarki o zmiennej prędkości
Technologia inwerterowa umożliwia pracę sprężarki z różnymi prędkościami, od niskich do wysokich, w zależności od zapotrzebowania na chłodzenie lub ogrzewanie. Gdy występuje duża różnica między żądaną temperaturą (nastawą) a rzeczywistą temperaturą w pomieszczeniu, sprężarka pracuje z większą prędkością, aby szybko schłodzić lub ogrzać pomieszczenie.
Gdy temperatura w pomieszczeniu zbliża się do wartości zadanej, sprężarka zwalnia, utrzymując stałą temperaturę bez konieczności częstego włączania i wyłączania. Praca ze zmienną prędkością ma kilka zalet:
- Bardziej stabilne i stałe temperatury: System utrzymuje bardziej stałą temperaturę, unikając wahań temperatury typowych dla tradycyjnych systemów.
- Zmniejszone zużycie energii: Pracując z niższymi prędkościami, gdy jest to możliwe, system zużywa mniej energii, co skutkuje niższymi rachunkami za media.
- Cichsza praca: Sprężarki o zmiennej prędkości obrotowej są generalnie cichsze niż sprężarki o stałej prędkości obrotowej, zwłaszcza podczas pracy przy niższych prędkościach.
- Dłuższa żywotność sprężarki: Zmniejszona liczba cykli włączania i wyłączania mniej obciąża sprężarkę, potencjalnie wydłużając jej żywotność.
Zaawansowane rozważania dotyczące rozmiaru
Technologia inwerterowa zapewnia również większą elastyczność w doborze wielkości systemów mini-split. Tradycyjne systemy o stałej prędkości wymagają precyzyjnego doboru, aby uniknąć problemów, takich jak krótkie cykle lub niewystarczające chłodzenie. Systemy z inwerterem mogą jednak działać wydajnie w szerszym zakresie wydajności.
Szukasz rozwiązań energooszczędnych aktywowanych ruchem?
Skontaktuj się z nami, aby uzyskać kompletne czujniki ruchu PIR, produkty energooszczędne aktywowane ruchem, przełączniki czujników ruchu i rozwiązania komercyjne w zakresie obecności/pobytu.
Niemniej jednak, prawidłowe dobranie rozmiaru pozostaje ważne dla optymalnej wydajności i efektywności. Zaawansowane aspekty doboru wielkości dla systemów z inwerterem obejmują:
- Wydajność przy częściowym obciążeniu: Ocena efektywności działania systemu przy ograniczonej wydajności jest kluczowa, ponieważ to właśnie tam będzie on spędzał większość swojego czasu.
- Współczynnik zwrotu: Odnosi się to do minimalnej wydajności, przy której system może działać. Niższy współczynnik wyłączenia pozwala na bardziej precyzyjną kontrolę temperatury i większą wydajność przy niskich obciążeniach.
- Rozmiar dostosowany do klimatu: Wydajność należy dostosować w oparciu o lokalne warunki klimatyczne i liczbę stopniodni grzania/chłodzenia.
- Analiza przegród zewnętrznych budynku: Ocena wpływu izolacji, uszczelnienia powietrza i wydajności okien na obciążenie chłodnicze pomaga określić odpowiedni rozmiar systemu.
- Wzorce obłożenia: Uwzględnienie sposobu wykorzystania przestrzeni i liczby osób przebywających w pomieszczeniu pomaga dostosować obliczenia rozmiaru.
Zalety klimatyzatorów typu Mini Split
Klimatyzatory typu minisplit oferują szereg istotnych korzyści, które czynią je atrakcyjną opcją dla wielu właścicieli domów:
Efektywność energetyczna
Mini-splity słyną z wysokiej efektywności energetycznej w porównaniu z tradycyjnymi systemami HVAC. Często mogą pochwalić się wyższymi wskaźnikami SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio), często przekraczającymi 20. Dla kontekstu, wyższa ocena SEER oznacza większą efektywność energetyczną. Technologia inwerterowa odgrywa znaczącą rolę w tej wydajności, umożliwiając precyzyjną kontrolę temperatury i zmniejszone zużycie energii.
Co więcej, bezkanałowa konstrukcja eliminuje straty energii związane z nieszczelnymi kanałami, co jest częstym problemem w centralnych systemach klimatyzacji. Strefowe chłodzenie dodatkowo zwiększa wydajność, umożliwiając ukierunkowane klimatyzowanie zajętych przestrzeni, zmniejszając straty energii związane z chłodzeniem lub ogrzewaniem niezajętych obszarów.
Chłodzenie strefowe
Jedną z najważniejszych zalet mini-splitów jest możliwość chłodzenia strefowego. Każda jednostka wewnętrzna może być sterowana niezależnie, umożliwiając ustawienie różnych temperatur dla różnych stref lub pomieszczeń. Nie tylko poprawia to komfort, dostosowując się do indywidualnych preferencji, ale także zmniejsza zużycie energii, klimatyzując tylko zajęte obszary.
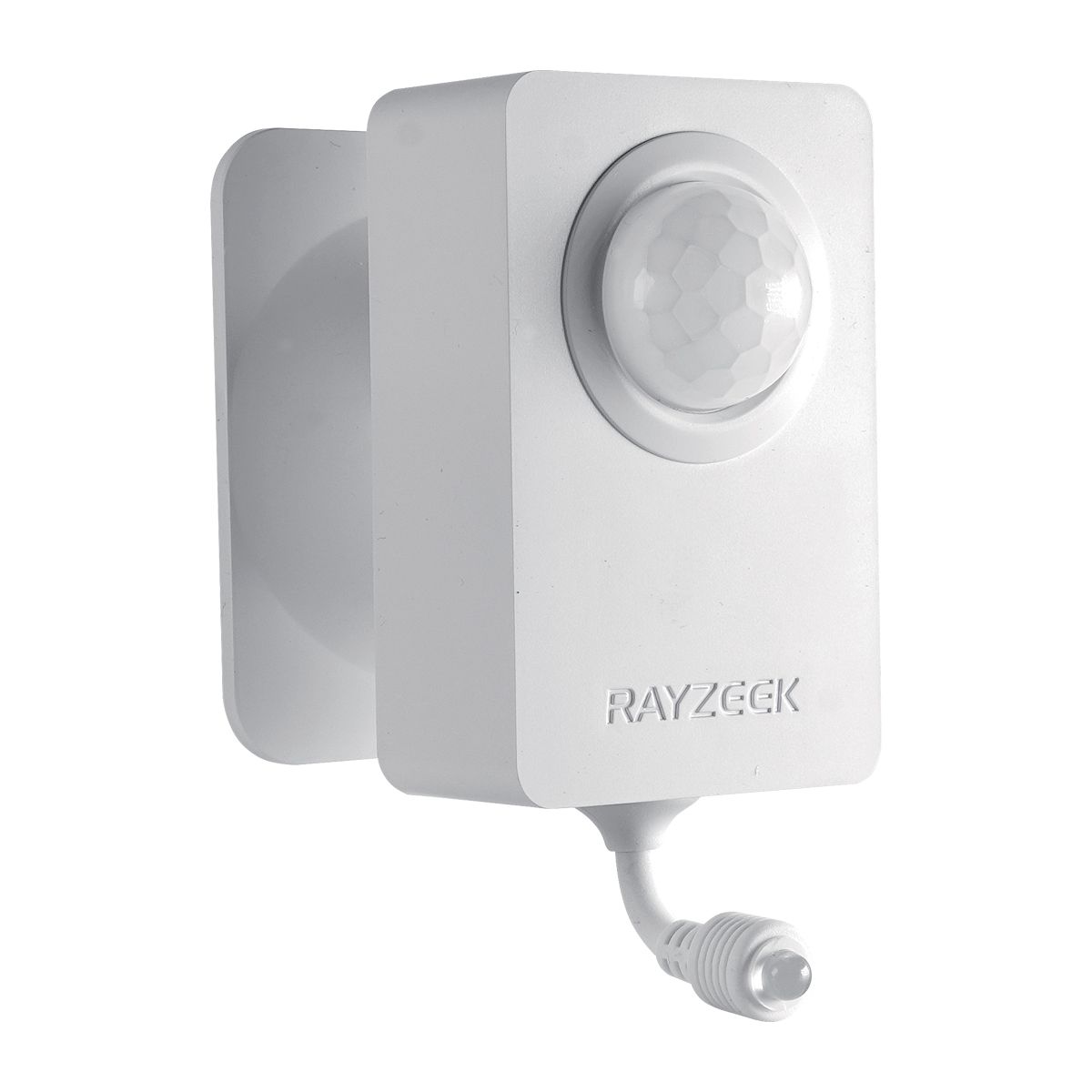
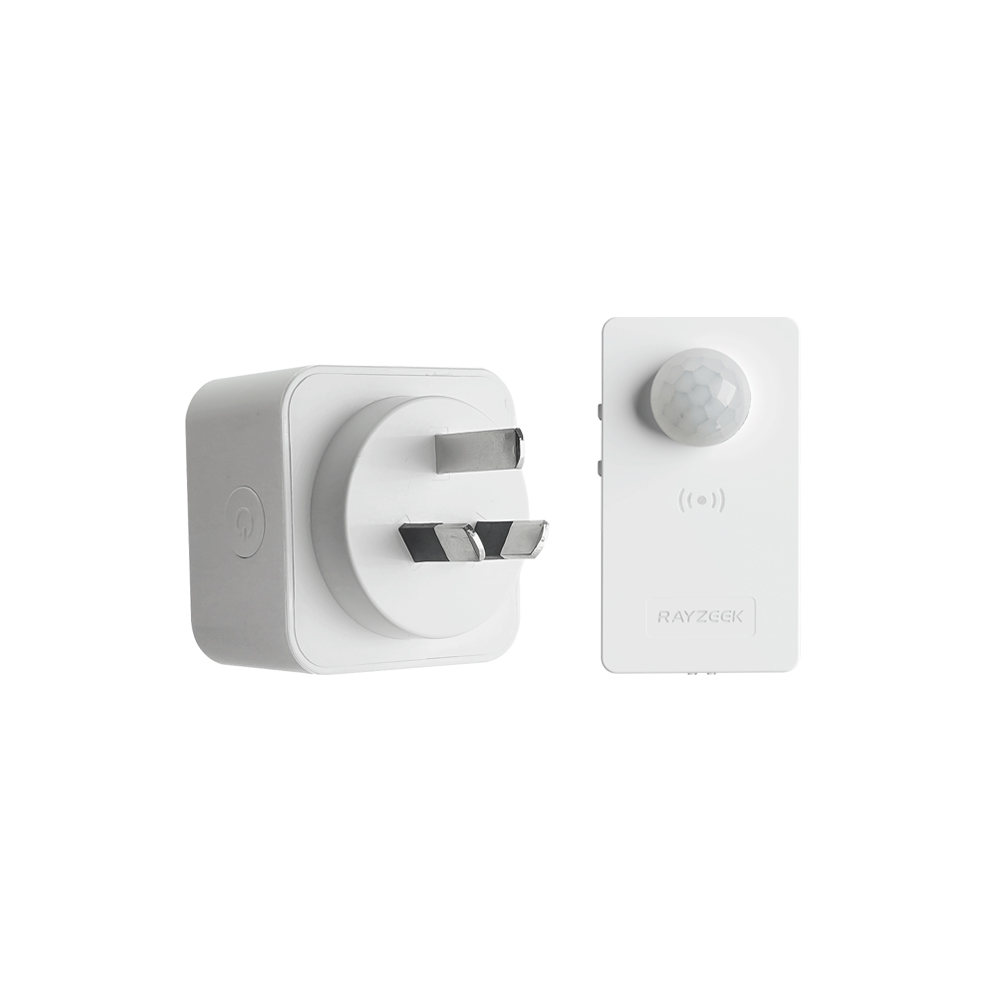
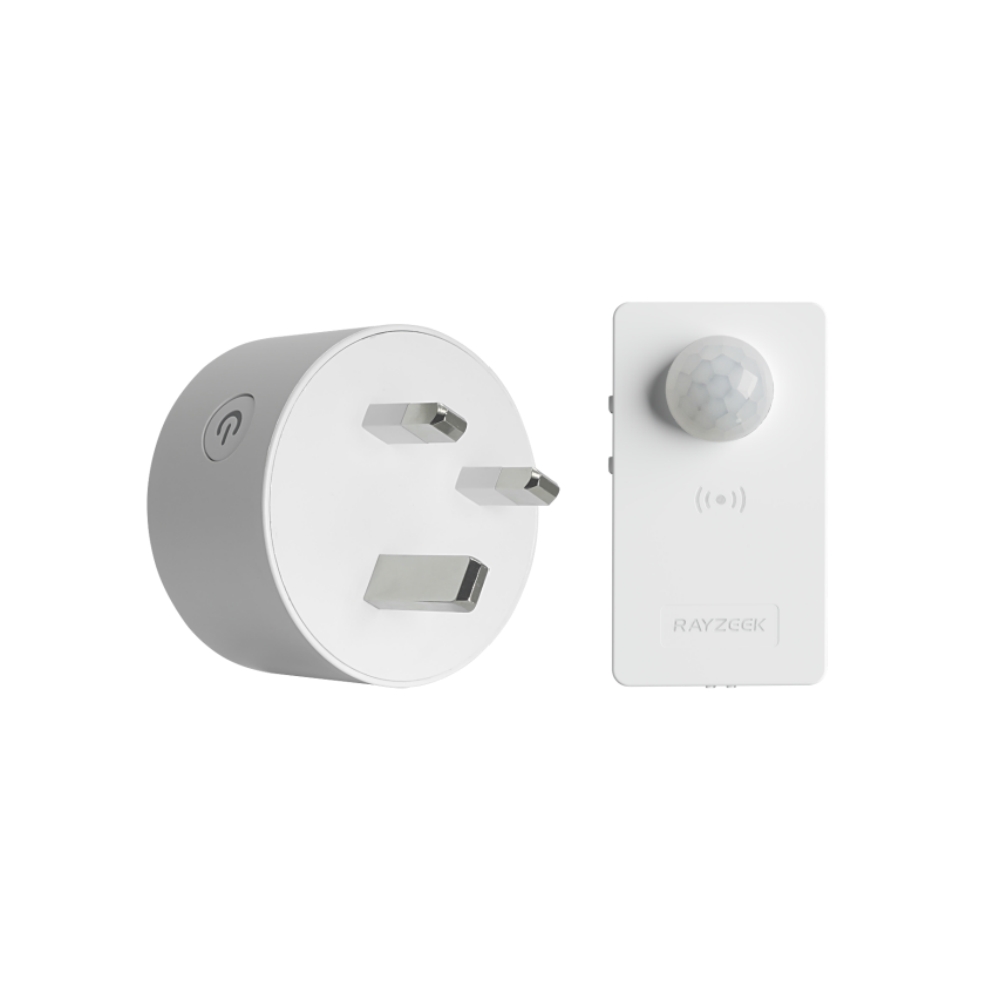
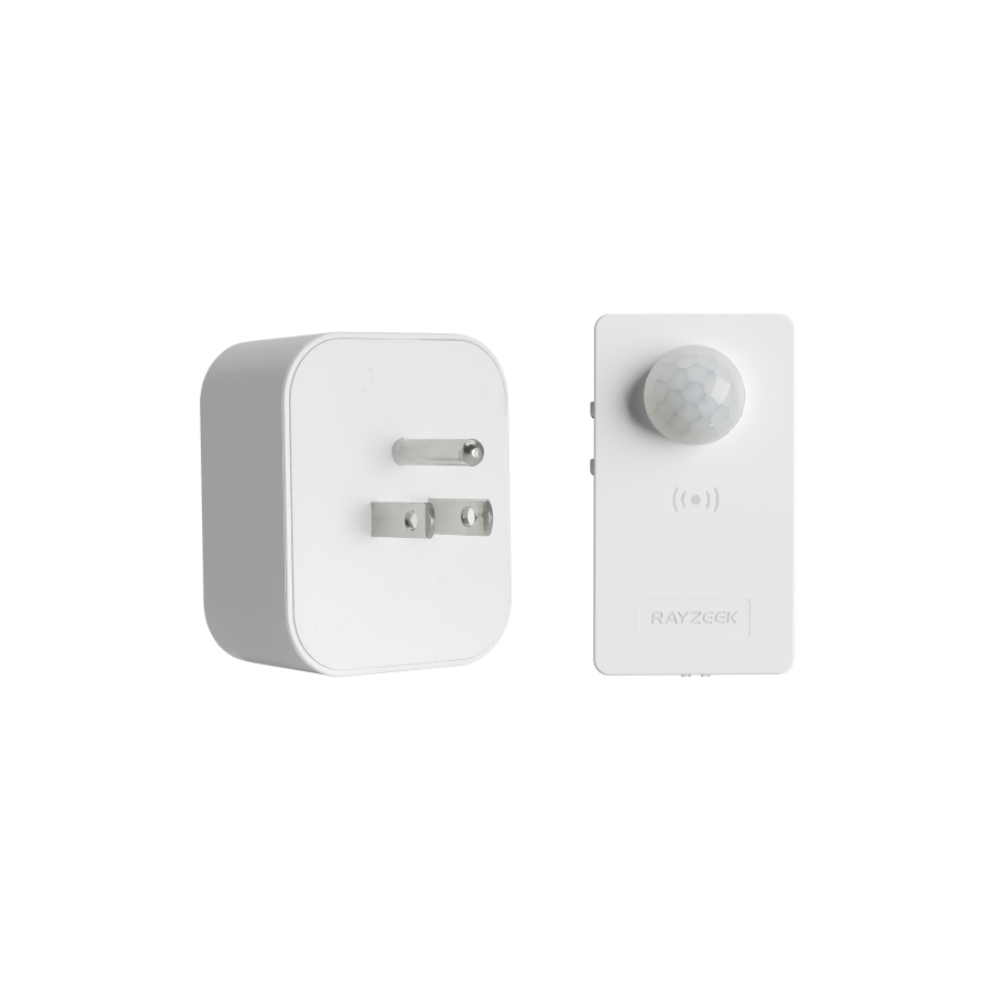
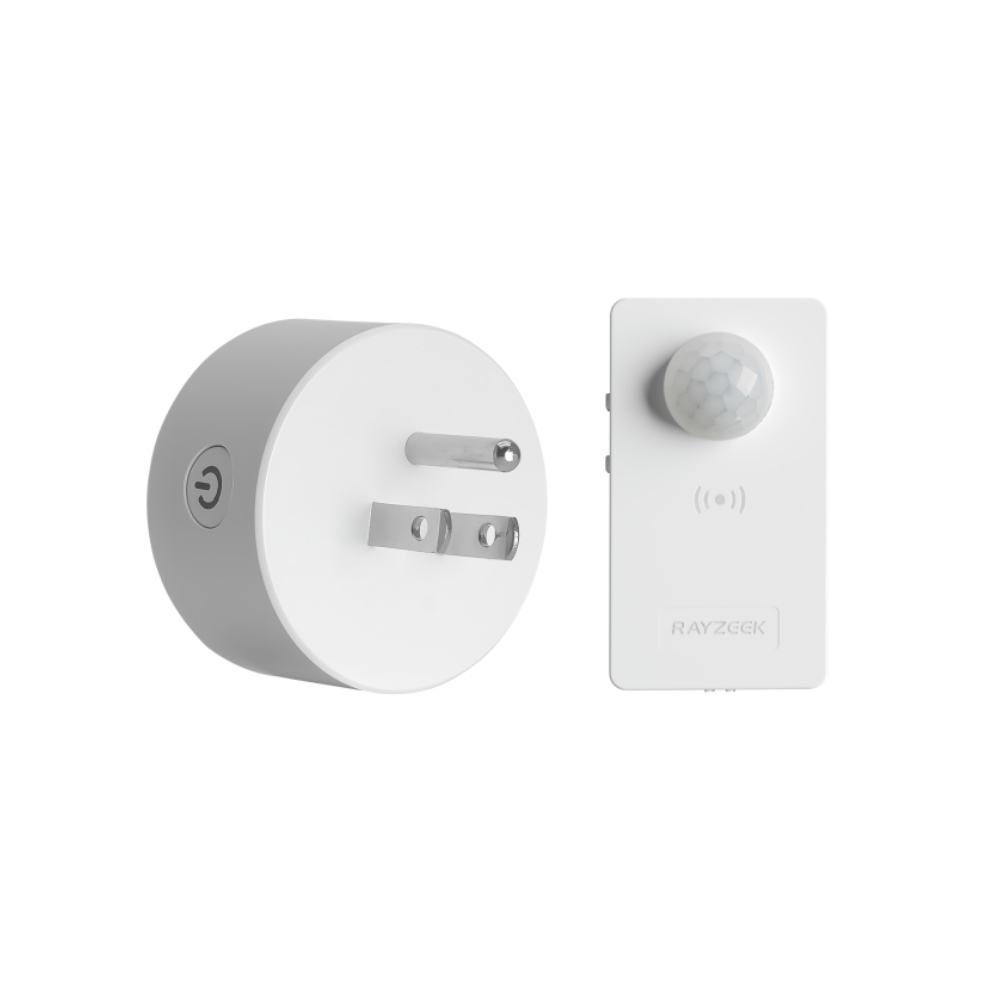
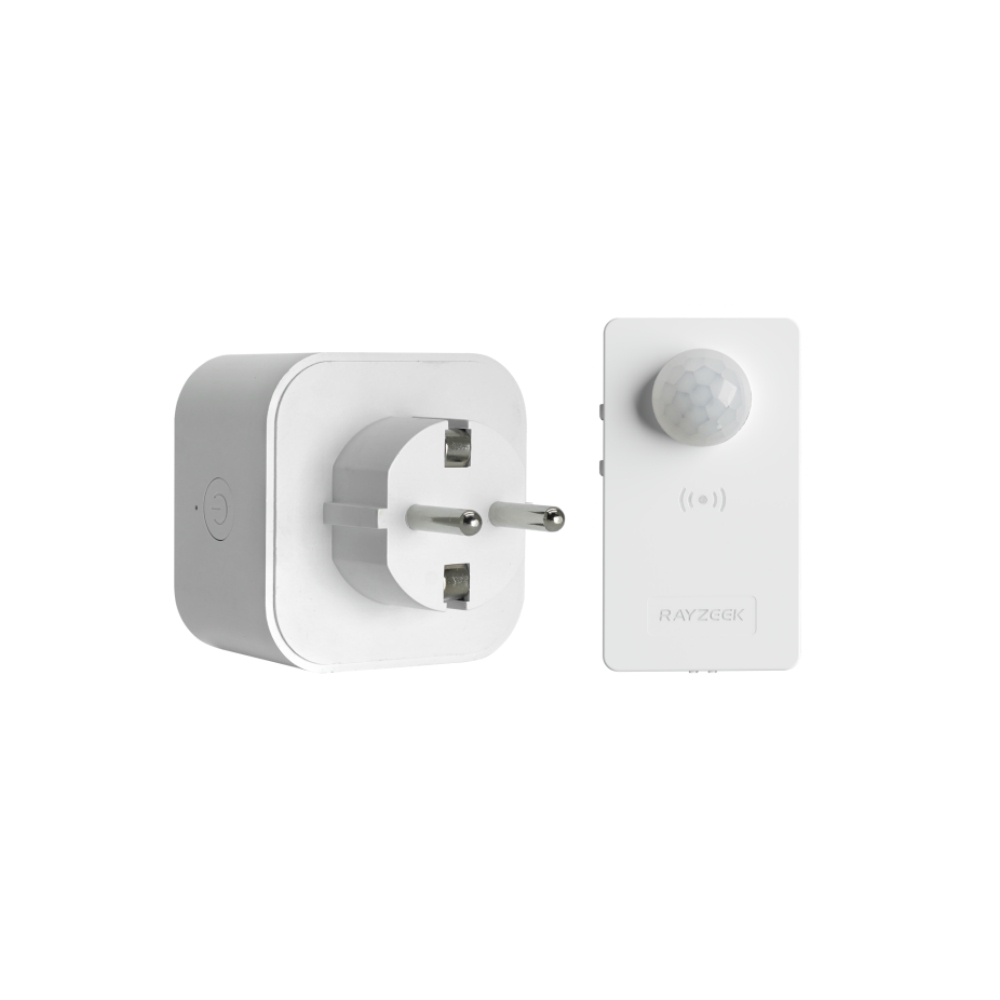
Pomyśl o tym: po co chłodzić cały dom do tej samej temperatury, gdy używasz tylko kilku pomieszczeń? Chłodzenie strefowe eliminuje potrzebę chłodzenia lub ogrzewania nieużywanych pomieszczeń, co prowadzi do znacznych oszczędności energii. Jednak nawet przy takim poziomie kontroli, łatwo jest zapomnieć o wyłączeniu klimatyzacji po opuszczeniu pokoju, zwłaszcza w ruchliwym domu lub biurze. W tym miejscu inteligentna automatyzacja może naprawdę wiele zmienić. Na przykład, urządzenie takie jak Czujnik ruchu klimatyzatora RZ050 może automatycznie wyłączyć mini-split, gdy pomieszczenie nie jest zajęte, zapewniając, że nie marnujesz energii na chłodzenie pustej przestrzeni. Ta dodatkowa warstwa automatyzacji maksymalizuje potencjał oszczędzania energii systemu mini-split, zapewniając zarówno wygodę, jak i spokój ducha.
Czujnik ruchu klimatyzatora RZ050
Nigdy więcej nie zapomnij wyłączyć klimatyzacji
- Automatycznie wyłącza klimatyzację w pustych pomieszczeniach, oszczędzając energię.
- Kompatybilny z większością jednostek split AC.
- Łatwy montaż DIY - wystarczy przykleić lub przykręcić do ściany.
Cicha praca
Mini-splity są znacznie cichsze niż jednostki okienne i wiele centralnych systemów klimatyzacji. Jednostki wewnętrzne pracują przy wyjątkowo niskim poziomie hałasu, często nawet 19 decybeli, co jest porównywalne z szelestem liści. Jednostki zewnętrzne są również zaprojektowane do cichej pracy, minimalizując zanieczyszczenie hałasem.
Technologia inwerterowa dodatkowo przyczynia się do cichej pracy, redukując wahania hałasu związane z cyklami włączania i wyłączania tradycyjnych sprężarek. Sprawia to, że mini-splity są doskonałym wyborem do sypialni, salonów i wszelkich pomieszczeń, w których hałas jest istotny.
Łatwa instalacja
W porównaniu z rozległymi przewodami wymaganymi przez centralne systemy klimatyzacji, mini-splity są stosunkowo łatwe w instalacji. Skraca to zarówno czas, jak i koszty instalacji. Instalacja zazwyczaj wymaga jedynie niewielkiego otworu w ścianie, aby pomieścić przewody czynnika chłodniczego, spust kondensatu i okablowanie elektryczne.
Ta łatwość instalacji sprawia, że mini-splity są opłacalną opcją dla różnych lokalizacji, w tym starszych domów bez istniejących kanałów, nowych dodatków, a nawet pojedynczych pomieszczeń, które wymagają dodatkowego chłodzenia lub ogrzewania.
Wady klimatyzatorów typu mini split
Chociaż mini-splity oferują liczne zalety, istnieją również pewne potencjalne wady, które należy wziąć pod uwagę:
Wyższy koszt początkowy
Mini-splity mają zazwyczaj wyższy koszt początkowy w porównaniu do jednostek okiennych lub niektórych podstawowych systemów centralnego powietrza. Ważne jest jednak, aby wziąć pod uwagę długoterminowe oszczędności energii, które często mogą z czasem zrównoważyć początkową inwestycję. Koszt może się różnić w zależności od takich czynników, jak liczba stref, wydajność systemu i jego funkcje.
Kwestie estetyczne
Wygląd jednostek wewnętrznych może być problemem dla niektórych właścicieli domów, zwłaszcza w mniejszych pomieszczeniach. Jednostki naścienne są najpopularniejszym typem, ale mogą one zakłócać estetykę pomieszczenia. Dostępne są alternatywne opcje montażu, takie jak kasety sufitowe lub jednostki podłogowe, ale mogą one wiązać się z wyższą ceną.
Umieszczenie jednostki zewnętrznej należy również rozważyć pod kątem wpływu na wygląd. Chociaż generalnie są one zaprojektowane tak, aby nie rzucały się w oczy, nadal muszą być umieszczone w dostępnym i dobrze wentylowanym miejscu.
Proces instalacji Mini Split
Podczas gdy niektórzy właściciele domów mogą pokusić się o samodzielną instalację, profesjonalna instalacja jest wysoce zalecana dla optymalnej wydajności, bezpieczeństwa i ochrony gwarancyjnej. Wykwalifikowany technik HVAC upewni się, że system jest odpowiednio dobrany, zainstalowany i skonfigurowany.
Typowe kroki instalacji obejmują:
- Ocena lokalizacji i obliczenie obciążenia: Technik oceni dom i wykona obliczenia obciążenia, aby określić odpowiedni rozmiar i konfigurację systemu.
- Montaż jednostek wewnętrznych: Jednostki wewnętrzne zostaną zamontowane na ścianie, suficie lub podłodze, w zależności od modelu i preferencji użytkownika.
- Instalacja jednostki zewnętrznej: Jednostka zewnętrzna zostanie zainstalowana na stabilnej, równej powierzchni, takiej jak betonowa podkładka, w dobrze wentylowanym miejscu.
- Wiercenie otworów na połączenia: W ścianie zostanie wywiercony niewielki otwór, zwykle o średnicy 3 cali, w którym zostaną umieszczone przewody czynnika chłodniczego, spust kondensatu i okablowanie elektryczne.
- Podłączanie przewodów czynnika chłodniczego: Przewody czynnika chłodniczego zostaną starannie połączone między jednostką wewnętrzną i zewnętrzną, tworząc szczelną pętlę.
- Instalacja przewodu odprowadzania skroplin: Przewód odprowadzania skroplin zostanie zainstalowany w celu odprowadzania skroplin z jednostki wewnętrznej.
- Podłączanie przewodów elektrycznych: Okablowanie elektryczne zostanie podłączone zgodnie ze specyfikacjami producenta i lokalnymi przepisami elektrycznymi.
- Ewakuacja przewodów czynnika chłodniczego: Przewody czynnika chłodniczego zostaną opróżnione za pomocą pompy próżniowej w celu usunięcia powietrza i wilgoci, zapewniając optymalną wydajność.
- Napełnianie układu czynnikiem chłodniczym: System zostanie napełniony odpowiednią ilością czynnika chłodniczego.
- Testowanie systemu: Technik dokładnie przetestuje system, aby upewnić się, że działa on prawidłowo i wydajnie.
Czas instalacji może się różnić w zależności od złożoności systemu, ale zazwyczaj zajmuje 4-8 godzin dla systemu jednostrefowego.
Ile kosztuje mini split?
Koszt systemu mini-split może się znacznie różnić w zależności od kilku czynników:
- Liczba stref: Systemy wielostrefowe są droższe niż systemy jednostrefowe.
- Wydajność systemu (BTU): Systemy o wyższej wydajności kosztują więcej.
- Marka i model: Różne marki i modele mają różne ceny.
- Ocena SEER: Wyższe oceny SEER zazwyczaj wiążą się z wyższą ceną, ale oferują większe długoterminowe oszczędności energii.
- Cechy: Zaawansowane funkcje, takie jak inteligentne sterowanie i ulepszona filtracja, mogą zwiększyć koszty.
- Złożoność instalacji: Bardziej złożone instalacje mogą wiązać się z wyższymi kosztami robocizny.
Średnie zakresy kosztów:
- System jednostrefowy: \$3,000 - \$6,000 zainstalowane
- System wielostrefowy (2-3 strefy): \$5,000 - \$10,000 zainstalowany
- System wielostrefowy (4-5 stref): \$8,000 - \$15,000+ zainstalowane
Dodatkowe koszty mogą obejmować modernizację elektryczną, pozwolenia i rozszerzone gwarancje. Choć koszty początkowe mogą wydawać się wysokie, należy wziąć pod uwagę długoterminowe oszczędności energii. W porównaniu z mniej wydajnymi opcjami chłodzenia, mini-splity mogą z czasem znacznie obniżyć rachunki za media, pomagając zrównoważyć początkową inwestycję.
Konserwacja mini split
Regularna konserwacja jest niezbędna, aby system mini-split działał wydajnie, zapobiegał awariom i wydłużał jego żywotność.
Zalecane zadania konserwacyjne:
- Wyczyść lub wymień filtry powietrza: Jest to prawdopodobnie najważniejsze zadanie konserwacyjne. Zanieczyszczone filtry powietrza ograniczają przepływ powietrza, zmniejszając wydajność i potencjalnie uszkadzając system. Filtry powinny być czyszczone lub wymieniane co 1-3 miesiące, w zależności od użytkowania i jakości powietrza.
- Wyczyść cewki jednostki wewnętrznej: Kurz i zanieczyszczenia mogą gromadzić się na wężownicach jednostki wewnętrznej, zmniejszając ich zdolność do przenoszenia ciepła. Wężownice te powinny być czyszczone co roku lub w razie potrzeby.
- Wyczyść cewki jednostki zewnętrznej: Wężownice jednostki zewnętrznej również mogą ulec zabrudzeniu, zwłaszcza jeśli znajdują się w pobliżu drzew lub krzewów. Wężownice te powinny być czyszczone co roku lub w razie potrzeby, aby zapewnić prawidłowe przenoszenie ciepła.
- Sprawdź poziom czynnika chłodniczego: Poziomy czynnika chłodniczego powinny być okresowo sprawdzane przez wykwalifikowanego technika. Niski poziom czynnika chłodniczego może wskazywać na wyciek, który należy niezwłocznie naprawić.
- Sprawdź przewód spustowy kondensatu: Przewód odprowadzania skroplin powinien być regularnie sprawdzany, aby upewnić się, że jest czysty i drożny. Zatkany przewód odpływowy może prowadzić do uszkodzeń spowodowanych przez wodę i rozwoju pleśni.
- Sprawdź połączenia elektryczne: Połączenia elektryczne powinny być okresowo sprawdzane pod kątem szczelności i korozji. Luźne lub skorodowane połączenia mogą powodować problemy elektryczne i zmniejszać wydajność systemu.
- Profesjonalny tuning: Zaleca się, aby profesjonalny technik HVAC przeprowadzał coroczną regulację. Zazwyczaj obejmuje to kontrolę i czyszczenie wszystkich komponentów, sprawdzenie poziomu czynnika chłodniczego i upewnienie się, że system działa prawidłowo.
Właściwa konserwacja może pomóc zapobiec kosztownym naprawom, poprawić efektywność energetyczną i wydłużyć żywotność systemu mini-split, ostatecznie oszczędzając pieniądze w dłuższej perspektywie.
Porównania Mini Split
Aby lepiej zrozumieć wartość mini-splitów, porównajmy je z dwiema popularnymi alternatywami: klimatyzacją centralną i klimatyzatorami okiennymi.
Mini Split a centralna klimatyzacja
| Cecha | Mini Split | Centralna klimatyzacja |
|---|---|---|
| Kanały | Bezkanałowy | Wymaga instalacji kanałowej |
| Chłodzenie strefowe | Tak | Ograniczone (chyba że zainstalowano system podziału na strefy) |
| Efektywność energetyczna | Ogólnie wyższe (wyższe oceny SEER) | Ogólnie niższe (niższe oceny SEER) |
| Instalacja | Łatwiejsze, mniej uciążliwe | Bardziej złożona, wymaga instalacji kanałów |
| Koszt początkowy | Wyższy | Niższy (dla podstawowych systemów) |
| Koszt operacyjny | Niższy | Wyższy |
| Poziom hałasu | Niższy | Wyższy |
| Filtracja powietrza | Zależy od modelu, często dostępne są zaawansowane opcje | Różni się w zależności od typu filtra, zazwyczaj jest mniej zaawansowany |
| Estetyka | Jednostki wewnętrzne mogą przeszkadzać | Mniej rzucające się w oczy (otwory wentylacyjne w sufitach lub ścianach) |
Podsumowanie: Mini-splity generalnie oferują wyższą efektywność energetyczną, strefowe chłodzenie i cichszą pracę w porównaniu do centralnej klimatyzacji. Wiążą się one jednak z wyższymi kosztami początkowymi i mogą stanowić wyzwanie estetyczne ze względu na jednostki wewnętrzne. Centralna klimatyzacja jest bardziej ugruntowaną technologią i może być bardziej odpowiednia dla domów z istniejącą siecią kanałów.
Może jesteś zainteresowany
Mini Split a klimatyzatory okienne
| Cecha | Mini Split | Klimatyzator okienny |
|---|---|---|
| Instalacja | Bardziej złożona, wymaga profesjonalnej instalacji | Prostszy, może być zainstalowany samodzielnie |
| Wydajność | Znacznie wyższy | Niższy |
| Poziom hałasu | Znacznie ciszej | Noisier |
| Wydajność chłodzenia | Wyższy, może chłodzić większe obszary | Niższa, ograniczona do pokoju jednoosobowego |
| Estetyka | Mniej rzucający się w oczy (nie zasłania okna) | Zasłania widok z okna i światło |
| Bezpieczeństwo | Większe bezpieczeństwo | Może stanowić zagrożenie dla bezpieczeństwa (łatwiejsze do usunięcia z zewnątrz) |
| Koszt | Znacznie wyższy | Niższy |
| Filtracja powietrza | Ogólnie lepiej | Podstawowa filtracja |
Podsumowanie: Mini-splity zdecydowanie wygrywają z jednostkami okiennymi pod względem wydajności, poziomu hałasu, wydajności chłodzenia i estetyki. Jednostki okienne są jednak znacznie tańsze i łatwiejsze w instalacji, co czyni je popularnym wyborem dla konsumentów dbających o budżet lub tych, którzy potrzebują tymczasowego rozwiązania chłodzącego.
Czy minisplity są tego warte?
Mini-splity mogą być opłacalną inwestycją dla wielu właścicieli domów, szczególnie tych, którzy priorytetowo traktują efektywność energetyczną, strefową kontrolę temperatury i cichsze rozwiązanie chłodzące. Są one szczególnie odpowiednie dla starszych domów bez istniejącej sieci kanałów, nowych dodatków lub renowacji określonych pomieszczeń.
Czynniki, które należy wziąć pod uwagę przy podejmowaniu decyzji, czy mini-split jest odpowiedni dla Ciebie:
- Koszty początkowe a długoterminowe oszczędności: Należy dokładnie ocenić początkową inwestycję w stosunku do przewidywanych oszczędności energii w całym okresie eksploatacji systemu. W wielu przypadkach długoterminowe oszczędności mogą przewyższyć wyższe koszty początkowe.
- Klimat: Mini-splity są bardzo skuteczne w umiarkowanym klimacie. Jednak w ekstremalnie zimnych regionach mogą wymagać dodatkowego ogrzewania.
- Preferencje estetyczne: Należy rozważyć wpływ wizualny jednostek wewnętrznych i zewnętrznych. Jeśli estetyka ma duże znaczenie, należy zbadać alternatywne opcje montażu lub rozważyć inny typ systemu.
- Wymagania dotyczące instalacji: Ocena wykonalności i kosztów instalacji w konkretnym domu.
Wartość długoterminowa:
- Zwiększona wartość domu: Energooszczędne systemy HVAC, takie jak mini-splity, stają się coraz bardziej atrakcyjne dla potencjalnych nabywców domów, potencjalnie zwiększając wartość odsprzedaży domu.
- Wydłużona żywotność: Przy odpowiedniej konserwacji, mini-splity mogą działać przez 15-20 lat lub nawet dłużej, zapewniając niezawodne chłodzenie i ogrzewanie przez wiele lat.
- Zmniejszony ślad węglowy: Wyższa wydajność przekłada się na niższe zużycie energii i mniejszą emisję gazów cieplarnianych, przyczyniając się do bardziej zrównoważonej przyszłości.
Kto produkuje minisplity?
Wielu renomowanych producentów produkuje systemy mini-split, z których każdy ma swoje mocne strony i specjalizacje. Oto niektóre z najpopularniejszych i najbardziej cenionych marek:
- Daikin: Daikin, światowy lider w dziedzinie technologii HVAC, jest znany ze swojej innowacyjności, wysokiej sprawności i szerokiej gamy produktów. Często uważana jest za markę premium.
- Mitsubishi Electric: Mitsubishi Electric oferuje szeroką gamę systemów mini-split z zaawansowanymi funkcjami, wysoką wydajnością i reputacją niezawodności.
- Fujitsu: Firma Fujitsu jest znana z produkcji niezawodnych i energooszczędnych urządzeń typu mini-splits z naciskiem na cichą pracę. Oferuje różnorodne modele dostosowane do różnych potrzeb i budżetów.
- LG: LG oferuje szereg modeli mini-split o eleganckim wyglądzie, inteligentnej integracji technologii i konkurencyjnych cenach.
- Gree: Gree, główny producent mini-splitów, oferuje szeroki wybór opcji w różnych przedziałach cenowych, co czyni je popularnym wyborem dla konsumentów dbających o budżet.
- Przewoźnik: Carrier, uznana marka HVAC, oferuje również systemy mini-split, wykorzystując swoje bogate doświadczenie i reputację w branży.
- Panasonic: Firma Panasonic znana jest z innowacyjnych i energooszczędnych systemów mini-splits, często wyposażonych w zaawansowaną technologię oczyszczania powietrza.
Wybierając markę, należy wziąć pod uwagę następujące kwestie:
- Reputacja i niezawodność: Sprawdź historię marki i przeczytaj opinie klientów, aby ocenić ich reputację w zakresie jakości i niezawodności.
- Zakres produktów: Upewnij się, że marka oferuje różnorodne modele, które spełniają określone potrzeby pod względem wydajności, funkcji i estetyki.
- Gwarancja: Porównaj warunki gwarancji i zakres oferowany przez różne marki. Dłuższa gwarancja może zapewnić spokój ducha i chronić inwestycję.
- Sieć dealerów: Wybierz markę z silną siecią wykwalifikowanych instalatorów i techników serwisowych w Twojej okolicy. Zapewni to dostęp do niezawodnego wsparcia w razie potrzeby.
- Cena: Porównaj ceny różnych marek i modeli o podobnych funkcjach i wydajności.
Ostatecznie kluczowe znaczenie ma współpraca z wykwalifikowanym wykonawcą HVAC, który może pomóc w wyborze odpowiedniej marki i modelu dla Twojego domu oraz zapewnić prawidłową instalację. Mogą oni ocenić konkretne potrzeby, polecić najlepszy system oraz zapewnić fachową instalację i bieżącą konserwację.