Have you ever wondered about the lifespan of your air conditioner’s components? This article will give you a comprehensive look at AC capacitors, which are essential to your AC system’s operation. We’ll explore everything about these components, from what they do and the different kinds available, to why they sometimes fail, what affects how long they last, and even how you might be able to extend their life. Whether you’re just curious about your AC or you’re a professional in the field, we’ve got you covered. The AC capacitor, though often overlooked, is actually a pretty critical part. And surprisingly, capacitor failure is a common reason why AC units malfunction. In fact, industry estimates suggest that about 7-10% of all residential AC service calls are due to capacitor failures. That’s why understanding this component and its potential issues is so important.
Τι είναι ένας πυκνωτής κλιματιστικού;
Λοιπόν, τι ακριβώς είναι an air conditioner capacitor? It’s an electrical component that stores energy in an electric field. This field is created between two conductive plates, usually made of metal, that are separated by an insulating material called the dielectric. Think of it like this: the capacitor stores energy electrostatically, much like a battery. But unlike a battery, which stores energy chemically, a capacitor can release its stored energy much faster. This makes it perfect for providing short bursts of high power.
Why is this important? Well, this stored energy can be rapidly discharged, giving a necessary power boost to components in your AC unit. Specifically, the capacitor provides that initial “kick” to start the AC’s motors, including the compressor motor and the fan motor. The compressor motor needs a significant burst of energy to get going and compress the refrigerant. The fan motor also needs to quickly reach operational speed to circulate air effectively.
Now, some capacitors, called run capacitors, also help the motors run περισσότερο efficiently after they’ve started. They do this by providing a consistent voltage and creating a phase shift between the motor windings, which optimizes the motor’s performance. And why is motor efficiency important? Because it means reduced energy consumption and less wear and tear on the motor, which can potentially extend its lifespan. Understanding all this is crucial to understanding why a capacitor’s failure can really impact your AC unit’s operation.
The capacitor is absolutely essential for your AC unit to start and run correctly. To understand why, think of the AC capacitor like the starter motor in your car. The starter motor provides the initial power to crank the engine. Similarly, the AC capacitor provides the initial power to start the compressor and fan motors in your AC unit. Without a functioning starter motor, your car’s engine simply won’t turn over. And just like that, without a working capacitor, your AC unit either won’t start at all or will really struggle to get going. This can lead to your AC failing to cool your home, and the struggling motor can even be damaged from overheating or excessive strain.
It’s important to understand that the capacitor’s job is different from other key AC components. The capacitor starts the compressor. The compressor itself is then responsible for circulating refrigerant throughout the system. The capacitor doesn’t actually interact with the refrigerant; it just provides the power to the motor that drives the compressor, which then moves the refrigerant. And finally, the thermostat acts as the control center, signaling the need for cooling. The capacitor provides the necessary power to the motors to respond to that signal from the thermostat.
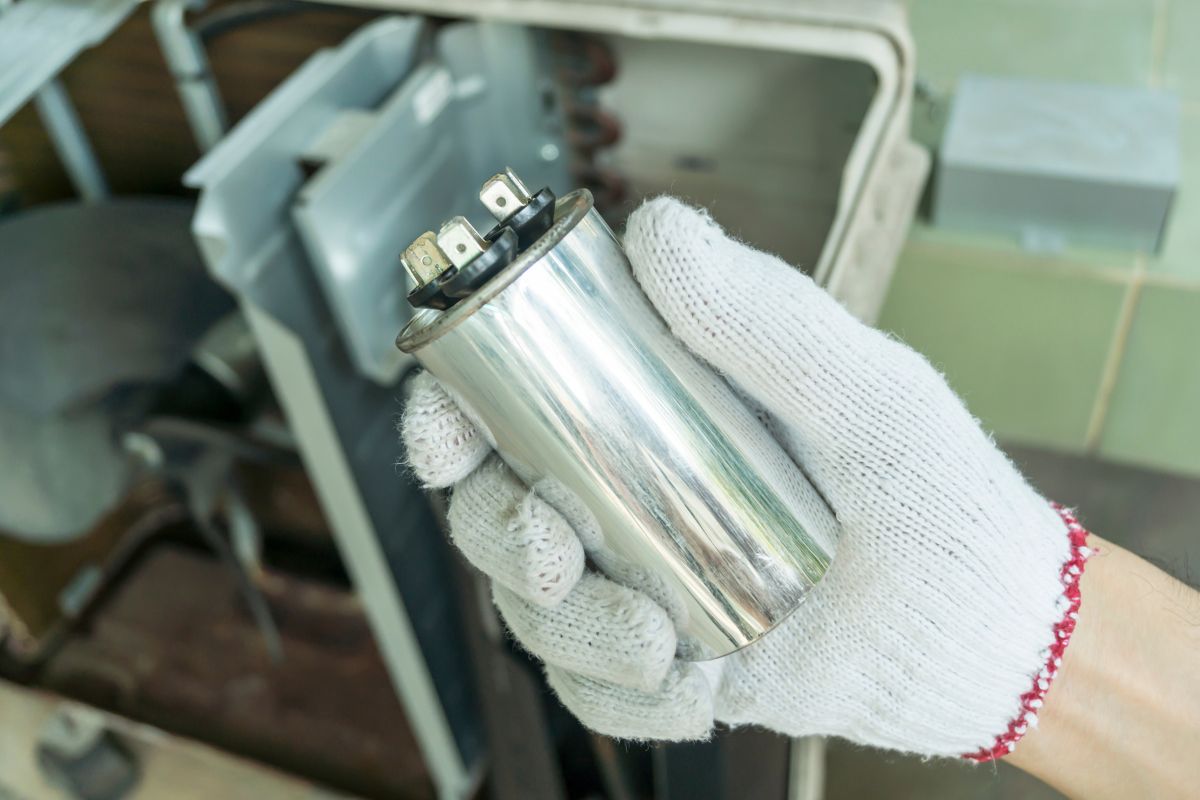
What does an AC capacitor actually look like? They’re usually cylindrical, though you might also see oval ones. The cylindrical shape is an efficient way to contain the internal components: those conductive plates and the dielectric material we talked about earlier. They’re encased in a protective housing, which can be metal (often aluminum) or plastic. Metal casings are generally more durable and help dissipate heat better. However, plastic casings can be more resistant to corrosion, especially in humid environments or places where they might be exposed to corrosive substances.
You’ll also notice that capacitors have terminals for electrical connections. Depending on the type of capacitor, there will be two or three terminals. These terminals are clearly labeled to show their function and polarity (if applicable). Common markings include “C” for common, “H” or “Herm” for the hermetic compressor connection, and “F” for the fan connection. It’s πραγματικά important to understand these markings because incorrect wiring can damage the capacitor, the motor it’s connected to, or even both!
Types of AC Capacitors
Start Capacitors
Okay, let’s dive into the different types of AC capacitors, starting with start capacitors. As the name suggests, these capacitors are designed to provide a large, short burst of electrical energy to start an AC motor, typically the compressor motor. Think of it like needing a really strong, initial push to get a heavy object moving from a standstill.
Technically speaking, start capacitors have high capacitance values, usually ranging from 70 to 1200 microfarads (µF). The symbol “µF” stands for microfarad, which is a unit of electrical capacitance. To give you some perspective, one farad is a τεράστια unit of capacitance, so capacitors in electronics and electrical systems usually have values measured in microfarads (millionths of a farad) or even picofarads (trillionths of a farad). Start capacitors also have relatively low voltage ratings compared to run capacitors, which we’ll discuss next.
Why the high capacitance? Well, it’s needed to store a large amount of energy for that initial motor start, providing the necessary torque to get things moving. And why is the energy delivery a short burst? Because prolonged use would overheat and damage the capacitor. Start capacitors are designed to prioritize high energy storage over continuous operation. You’ll typically find them used for the compressor motor in most residential AC units.
Start capacitors are usually electrolytic capacitors. Electrolytic capacitors offer a high capacitance value in a relatively small and cost-effective package. However, they’re generally more prone to failure than other types, like film capacitors, due to their internal construction and the chemical processes involved.
Run Capacitors
Next up are run capacitors. Unlike start capacitors, run capacitors provide a continuous, smaller supply of energy to help keep the motor running smoothly after it’s already started. They constantly charge and discharge in sync with the AC power cycle. Think of it like a steady stream of fuel that keeps an engine running smoothly after you’ve turned the key.
Run capacitors have lower capacitance values, typically ranging from 2.5 to 100 µF, but they have higher voltage ratings compared to start capacitors. The lower capacitance is sufficient because the run capacitor only needs to provide a small, continuous boost to maintain the motor’s operation, rather than a large initial surge. The higher voltage rating is necessary because the run capacitor needs to withstand continuous operation at the AC unit’s voltage without breaking down.
You’ll find run capacitors used for both compressor and fan motors in AC units. They’re usually metallized polypropylene film capacitors. Metallized polypropylene film capacitors are more durable and reliable for continuous operation than electrolytic capacitors. They offer a longer lifespan, are less prone to failure, and can handle higher operating temperatures.
Dual-Run Capacitors
Finally, we have dual-run capacitors. These capacitors combine the functions of both a start capacitor and a run capacitor into a single unit. How do they work? A dual-run capacitor has three terminals: one labeled “C” for common, one labeled “Fan” for the fan motor connection, and one labeled “Herm” (or “H”) for the hermetic compressor motor connection. The presence of these three terminals is the key to identifying a dual-run capacitor; single-run or start capacitors will only have two terminals.
Internally, a dual-run capacitor is essentially two capacitors—one designed for starting and one for running—packaged together in a single housing. You’ll commonly find dual-run capacitors in modern AC units. They save space and simplify the wiring within the AC unit by reducing the number of individual components. However, there’s a significant downside: if one part of the dual capacitor (either the start or run section) fails, the ολόκληρο το unit needs to be replaced, even if the other section is still working perfectly. So, if either the “start” or “run” section fails, the whole dual-run capacitor becomes useless.
Πώς λειτουργούν οι πυκνωτές AC
So, how do AC capacitors actually εργασία? The basic principle is capacitance, which is the ability of a component to store electrical charge. In a capacitor, this is done by having two conductive plates, usually made of metal, separated by an insulating material called the dielectric.
Imagine two parallel metal plates separated by a small gap filled with air or another insulating material. The larger the surface area of the plates, the higher the capacitance, meaning the capacitor can store more charge. Also, the smaller the distance between the plates, the higher the capacitance. The properties of the dielectric material also significantly affect capacitance. Different materials have different abilities to store electrical energy in an electric field.
The relationship between these factors is summarized by the formula: C = εA/d, where C is capacitance, ε (epsilon) is the permittivity of the dielectric (a measure of its ability to store electrical energy), A is the area of the plates, and d is the distance between the plates.
What happens when you apply voltage across the capacitor? Well, electrons start to accumulate on one of the conductive plates, creating a negative charge on that plate. Because opposite charges attract, an equal and opposite positive charge develops on the other plate. The dielectric material between the plates acts as an insulator, preventing the accumulated electrons from flowing directly across the gap to the positively charged plate. The dielectric’s properties determine how much charge can be stored at a given voltage.
Ψάχνετε για λύσεις εξοικονόμησης ενέργειας με ενεργοποίηση κίνησης;
Επικοινωνήστε μαζί μας για πλήρεις αισθητήρες κίνησης PIR, προϊόντα εξοικονόμησης ενέργειας με ενεργοποίηση κίνησης, διακόπτες με αισθητήρα κίνησης και εμπορικές λύσεις Occupancy/Vacancy.
The energy in a capacitor is stored in the electric field that’s created between the positively and negatively charged plates. Think of it like stretching a rubber band. The stretched rubber band stores potential energy, which can be released when you let go. Similarly, the capacitor stores electrical potential energy in the electric field. The amount of energy stored is given by the formula: E = 1/2CV², where E is energy, C is capacitance, and V is voltage.
So, when does a capacitor discharge? When the circuit needs a power boost, like when starting a motor. The stored energy is released as a flow of current from the negatively charged plate to the positively charged plate through the connected circuit. As we discussed earlier, start capacitors provide a rapid and high-current discharge to deliver the initial torque needed to start the motor. Run capacitors, on the other hand, provide a continuous, lower-current discharge to help maintain the motor’s operation after it has started.
Run capacitors also create a phase shift between the current and voltage in the motor windings. This phase shift is essential for the efficient operation of AC induction motors because it creates a rotating magnetic field, which is what drives the motor’s rotation.
It’s important to distinguish between AC and DC capacitors. AC capacitors are specifically designed to handle alternating current (AC), where the voltage polarity reverses periodically (for example, 60 times per second in a 60 Hz system). DC capacitors, on the other hand, are designed for direct current (DC) circuits where the voltage remains constant.
Why is this distinction important? Because DC capacitors are not suitable for AC applications. Using a DC capacitor in an AC circuit can lead to damage or even catastrophic failure of the capacitor. AC capacitors are typically non-polarized, meaning they can handle voltage applied in either direction without damage. While electrolytic capacitors (often used for start capacitors) are polarized, they’re used in AC motor-start circuits in a way that accounts for their polarity, typically involving brief application of voltage.
Typical AC Capacitor Lifespan
So, how long can you expect your AC capacitor to last? On average, an AC capacitor will generally last between 10 and 20 years. However, it’s important to remember that this is just a broad average and not a guarantee. Many factors, which we’ll discuss in detail later, can significantly shorten or extend this lifespan. The lifespan of capacitors isn’t always predictable; there can be a wide range of failure times, with some capacitors failing much earlier or later than the average.
It’s worth noting that capacitors often have a shorter lifespan than some other major AC components, like the compressor itself. This is significant because, as we mentioned earlier, capacitor failure is a relatively common reason for AC service calls. Fan motors may have a similar or slightly longer lifespan than capacitors, but it really depends on how they’re used, their quality, and the operating environment.
Where can you find reliable data on capacitor lifespan? You can check with HVAC manufacturers, industry associations like ACCA (Air Conditioning Contractors of America) and ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers), and independent testing laboratories.
While precise failure rate curves are often kept secret by manufacturers, the general pattern of capacitor failures often looks like a “bathtub curve.” What does that mean? Well, there’s a higher initial failure rate (called “infant mortality”) due to manufacturing defects or early-life weaknesses. Then, there’s a period of relatively low and constant failure rates during the capacitor’s “useful life.” Finally, the failure rate increases as the capacitor reaches the end of its lifespan due to wear and tear and, most importantly, dielectric degradation.
It can be tricky to get precise, publicly available data on capacitor failure rates because manufacturers often consider this information proprietary. However, the experience of HVAC technicians, while anecdotal, can provide valuable insights into common failure patterns and real-world lifespans. Just remember to consider this alongside more formal data from manufacturers and testing labs.
Keep in mind that manufacturers may give an “expected” lifespan for their capacitors, but this is often based on ideal operating conditions and might not reflect how it performs in the real world. The actual lifespan of a capacitor can be significantly affected by various factors, including operating conditions (temperature, load), how well you maintain your system, and environmental factors (humidity, dust). Understanding the difference between the expected lifespan under ideal conditions and the actual lifespan in your specific situation can help you manage your expectations, plan for potential replacements, and maybe even take steps to maximize the capacitor’s service life.
Γιατί αποτυγχάνουν οι πυκνωτές AC
Dielectric Degradation
So, what’s the main reason AC capacitors fail? It’s dielectric degradation. The dielectric is the insulating material located between the capacitor’s conductive plates. Over time, this material breaks down due to a combination of factors, including heat, voltage stress, and chemical reactions.
At a microscopic level, the dielectric’s molecular structure changes, which reduces its ability to effectively insulate and store electrical charge. This degradation leads to several consequences: reduced capacitance (meaning the capacitor can’t store as much energy), increased leakage current (which is the undesirable flow of current through the dielectric; ideally, it should be zero), and eventually, either a short circuit (where the plates effectively touch) or an open circuit (where the capacitor no longer conducts electricity).
The specific chemical reactions that cause degradation depend on the dielectric material used. In electrolytic capacitors, the electrolyte (a liquid or gel-like substance) can gradually dry out or undergo chemical changes due to heat and electrical stress. This leads to a decrease in capacitance and an increase in leakage current. In metallized polypropylene film capacitors, the degradation process is more complex. It can involve oxidation of the thin metallization layer on the film, chain scission (breaking of the long polymer chains) of the polypropylene molecules, and the formation of tiny voids (micro-voids) within the dielectric. These processes are accelerated by both heat and voltage stress.
Ίσως ενδιαφέρεστε για
Heat
Heat is a major contributor to capacitor failure, significantly speeding up the degradation process. Where does this heat come from? It can come from several sources: the ambient temperature around the AC unit, heat generated by other components within the AC unit, and heat generated internally within the capacitor due to its internal resistance (especially when it’s charging and discharging).
Heat speeds up the chemical reactions that break down the dielectric material, causing it to deteriorate faster than it would at lower temperatures. Capacitors have specified temperature ratings, and exceeding these ratings, even for short periods, can dramatically shorten the capacitor’s lifespan.
Voltage Fluctuations
Voltage fluctuations, especially voltage spikes and surges, can also damage the capacitor’s dielectric. These fluctuations can be caused by various events, including lightning strikes, problems with the power grid, faulty wiring in your building, or even the operation of other electrical equipment on the same circuit.
Voltage spikes can physically puncture or weaken the dielectric material, creating a pathway for current to flow between the plates, which leads to a short circuit. Both overvoltage (voltage exceeding the capacitor’s rating) and undervoltage (voltage below the required level) can be bad for your AC unit’s operation. However, overvoltage is generally more immediately damaging to the capacitor itself, potentially causing it to fail right away.
Manufacturing Defects
Although it’s less common than dielectric degradation caused by environmental or operational factors, manufacturing defects can also lead to premature capacitor failure. Examples of these defects include impurities in the dielectric material, poor sealing of the capacitor casing (which allows moisture or contaminants to enter), and loose or poorly made internal connections. Reputable capacitor manufacturers have strict quality control processes in place to minimize these defects.
Wear and Tear
Over time, the repeated charging and discharging cycles that a capacitor goes through can contribute to wear and tear, gradually degrading its performance. Electrolytic capacitors are particularly susceptible to wear and tear because of the chemical processes that happen inside them during operation. Film capacitors, like metallized polypropylene capacitors, are generally more resistant to wear and tear due to how they’re built and the materials used.
Παράγοντες που μειώνουν τη διάρκεια ζωής του πυκνωτή AC
Περιβαλλοντικοί παράγοντες
Αρκετοί περιβαλλοντικοί παράγοντες μπορούν να μειώσουν σημαντικά τη διάρκεια ζωής του πυκνωτή AC σας. Ας ρίξουμε μια ματιά σε μερικούς από τους πιο συνηθισμένους.
Υψηλές θερμοκρασίες περιβάλλοντος
Οι υψηλές θερμοκρασίες περιβάλλοντος είναι ένας major παράγοντας για τη μείωση της διάρκειας ζωής του πυκνωτή. Οι υψηλές θερμοκρασίες επιταχύνουν άμεσα τη διαδικασία υποβάθμισης του διηλεκτρικού, η οποία, όπως συζητήσαμε νωρίτερα, είναι ο κύριος λόγος αποτυχίας των πυκνωτών. Εάν ζείτε σε ένα θερμό κλίμα, όπως η Αριζόνα ή η Φλόριντα, η μονάδα AC σας θα έχει γενικά μικρότερη διάρκεια ζωής πυκνωτή σε σύγκριση με αυτές σε ψυχρότερα κλίματα, υποθέτοντας ότι όλα τα άλλα είναι ίσα. Τα καλά νέα είναι ότι ο σωστός αερισμός και η εξασφάλιση επαρκούς ροής αέρα γύρω από τη μονάδα AC σας μπορεί να βοηθήσει στη μείωση των επιπτώσεων των υψηλών θερμοκρασιών περιβάλλοντος. Θα μιλήσουμε περισσότερα για αυτό αργότερα.
Υψηλή υγρασία
Η υψηλή υγρασία μπορεί επίσης να επηρεάσει αρνητικά τη διάρκεια ζωής του πυκνωτή σας. Η υψηλή υγρασία μπορεί να προκαλέσει διάβρωση των ακροδεκτών του πυκνωτή και, σε σοβαρές περιπτώσεις, ακόμη και εσωτερικών εξαρτημάτων εάν εισχωρήσει υγρασία στο εσωτερικό του περιβλήματος. Αυτό είναι ιδιαίτερα προβληματικό στις παράκτιες περιοχές λόγω του αλατιού στον αέρα, το οποίο επιταχύνει τη διάβρωση. Η χρήση πυκνωτών με ανθεκτικά στη διάβρωση υλικά και η διασφάλιση ότι όλα είναι σωστά σφραγισμένα μπορεί να βοηθήσει στη μείωση των επιπτώσεων της υψηλής υγρασίας.
Διαβρωτικά περιβάλλοντα
Δεν είναι μόνο η υψηλή υγρασία. και άλλα διαβρωτικά περιβάλλοντα μπορούν επίσης να βλάψουν τους πυκνωτές. Όπως αναφέραμε νωρίτερα, οι παράκτιες περιοχές με αλμυρό αέρα είναι ένα χαρακτηριστικό παράδειγμα. Οι βιομηχανικές περιοχές με υψηλά επίπεδα ατμοσφαιρικών ρύπων μπορούν επίσης να δημιουργήσουν ένα διαβρωτικό περιβάλλον. Η χρήση σφραγισμένων πυκνωτών ή η παροχή προστατευτικών περιβλημάτων για τη μονάδα AC σας μπορεί να βοηθήσει στην προστασία του πυκνωτή σε αυτά τα περιβάλλοντα.
Σκόνη και υπολείμματα
Η συσσώρευση σκόνης και υπολειμμάτων στον πυκνωτή και τα γύρω εξαρτήματα μπορεί επίσης να μειώσει τη διάρκεια ζωής του. Η σκόνη και τα υπολείμματα λειτουργούν ως μονωτής, ο οποίος εμποδίζει τη διάχυση θερμότητας από τον πυκνωτή. Αυτό οδηγεί σε υψηλότερες θερμοκρασίες λειτουργίας, οι οποίες επιταχύνουν την υποβάθμιση του διηλεκτρικού. Ο τακτικός καθαρισμός της μονάδας AC σας, συμπεριλαμβανομένης της περιοχής γύρω από τον πυκνωτή, είναι ζωτικής σημασίας για την πρόληψη αυτού του προβλήματος.
Εμπνευστείτε από τα χαρτοφυλάκια αισθητήρων κίνησης Rayzeek.
Δεν βρίσκετε αυτό που θέλετε; Μην ανησυχείτε. Υπάρχουν πάντα εναλλακτικοί τρόποι για να λύσετε τα προβλήματά σας. Ίσως ένα από τα χαρτοφυλάκια μας μπορεί να σας βοηθήσει.
Λειτουργικοί παράγοντες
Εκτός από τις περιβαλλοντικές συνθήκες, ο τρόπος λειτουργίας και συντήρησης της μονάδας AC σας έχει επίσης μεγάλη επίδραση στη διάρκεια ζωής του πυκνωτή σας. Ας ρίξουμε μια ματιά σε ορισμένους βασικούς λειτουργικούς παράγοντες.
Συχνή ενεργοποίηση/απενεργοποίηση
Η συχνή ενεργοποίηση/απενεργοποίηση της μονάδας AC σας ασκεί σημαντική πίεση στον πυκνωτή. Κάθε φορά που ξεκινά η μονάδα AC, ο πυκνωτής υφίσταται μια αύξηση ρεύματος. Η σύντομη λειτουργία, όπου η μονάδα AC ενεργοποιείται και απενεργοποιείται πολύ γρήγορα, είναι ιδιαίτερα επιζήμια.
Γιατί η σύντομη λειτουργία είναι τόσο επιβλαβής; Επειδή ο πυκνωτής μπορεί να μην αποφορτιστεί πλήρως πριν επαναφορτιστεί, γεγονός που οδηγεί σε αυξημένη συσσώρευση θερμότητας και πίεση στο διηλεκτρικό υλικό. Οι συνήθεις αιτίες της σύντομης λειτουργίας περιλαμβάνουν μια υπερμεγέθη μονάδα AC για τον χώρο που ψύχεται, προβλήματα θερμοστάτη και διαρροές ψυκτικού.
Αιχμές και υπερτάσεις τάσης
Οι αιχμές και οι υπερτάσεις τάσης, όπως συζητήσαμε νωρίτερα, μπορούν να προκαλέσουν άμεση και καταστροφική ζημιά στον πυκνωτή. Αυτές οι ξαφνικές αυξήσεις της τάσης μπορούν να τρυπήσουν το διηλεκτρικό, οδηγώντας σε βραχυκύκλωμα. Η χρήση ενός προστατευτικού υπερτάσεων μπορεί να βοηθήσει στην προστασία της μονάδας AC σας, συμπεριλαμβανομένου του πυκνωτή, από αιχμές τάσης. Για ολοκληρωμένη προστασία, συνιστάται ένα προστατευτικό υπερτάσεων ολόκληρου του σπιτιού, επειδή προστατεύει όλα ηλεκτρικές συσκευές στο σπίτι σας, όχι μόνο η μονάδα AC σας.
Παρατεταμένη λειτουργία υπό βαρύ φορτίο
Η παρατεταμένη λειτουργία της μονάδας AC σας υπό βαρύ φορτίο μπορεί επίσης να μειώσει τη διάρκεια ζωής του πυκνωτή. Ένα βαρύ φορτίο σημαίνει ότι η μονάδα AC σας εργάζεται σκληρότερα και για μεγαλύτερες χρονικές περιόδους, γεγονός που παράγει περισσότερη θερμότητα. Εάν έχετε μια υπομεγέθη μονάδα AC για τον χώρο που ψύχετε, θα αναγκαστεί να εργαστεί σκληρότερα και περισσότερο, οδηγώντας σε υψηλότερες θερμοκρασίες λειτουργίας και αυξημένη πίεση στον πυκνωτή. Η κακή ροή αέρα γύρω από τη μονάδα AC, λόγω φραγμένων αεραγωγών ή βρώμικων πηνίων, περιορίζει την ψύξη και αυξάνει επίσης τις θερμοκρασίες λειτουργίας.
Ακατάλληλη εγκατάσταση
Η εσφαλμένη εγκατάσταση του πυκνωτή ή της ίδιας της μονάδας AC μπορεί να οδηγήσει σε πρόωρη αστοχία του πυκνωτή. Η εσφαλμένη καλωδίωση μπορεί να βλάψει τον πυκνωτή, τον κινητήρα ή και τα δύο. Οι χαλαρές συνδέσεις μπορεί να οδηγήσουν σε τόξο (ηλεκτρικοί σπινθήρες) και υπερθέρμανση, γεγονός που βλάπτει τον πυκνωτή. Η χρήση του λάθους τύπου πυκνωτή ή ενός με εσφαλμένη τάση ή χωρητικότητα μπορεί επίσης να τον κάνει να αποτύχει νωρίτερα από ό,τι θα έπρεπε.
Έλλειψη συντήρησης
Η έλλειψη τακτικής συντήρησης για τη μονάδα AC σας μπορεί να συμβάλει σε προβλήματα πυκνωτή. Τα βρώμικα πηνία συμπυκνωτή μειώνουν την ικανότητα της μονάδας να διαχέει θερμότητα, οδηγώντας σε υψηλότερες θερμοκρασίες λειτουργίας και αυξημένη πίεση στον πυκνωτή. Η αγνόηση των προειδοποιητικών σημάτων προβλημάτων AC, όπως ασυνήθιστοι θόρυβοι ή μειωμένη ικανότητα ψύξης, μπορεί να επιτρέψει σε μικρά προβλήματα να κλιμακωθούν σε μεγάλα προβλήματα, συμπεριλαμβανομένης της αστοχίας του πυκνωτή.
Αρμονική παραμόρφωση
Τέλος, ας μιλήσουμε για την αρμονική παραμόρφωση. Η αρμονική παραμόρφωση στην παροχή ηλεκτρικής ενέργειας μπορεί να επηρεάσει αρνητικά τη διάρκεια ζωής του πυκνωτή σας. Αυτή η παραμόρφωση προκαλείται από μη γραμμικά φορτία, όπως ορισμένοι τύποι ηλεκτρονικού εξοπλισμού, τα οποία αντλούν ρεύμα σε σύντομους παλμούς και όχι σε ένα ομαλό ημιτονοειδές κύμα. Αυτοί οι παλμοί εισάγουν ρεύματα υψηλότερης συχνότητας στην κυκλωματολογία της μονάδας AC σας. Αυτά τα ρεύματα υψηλότερης συχνότητας μπορούν να αυξήσουν την πίεση στον πυκνωτή, ιδιαίτερα στους πυκνωτές λειτουργίας, οδηγώντας σε αυξημένη παραγωγή θερμότητας και επιταχυνόμενη υποβάθμιση.