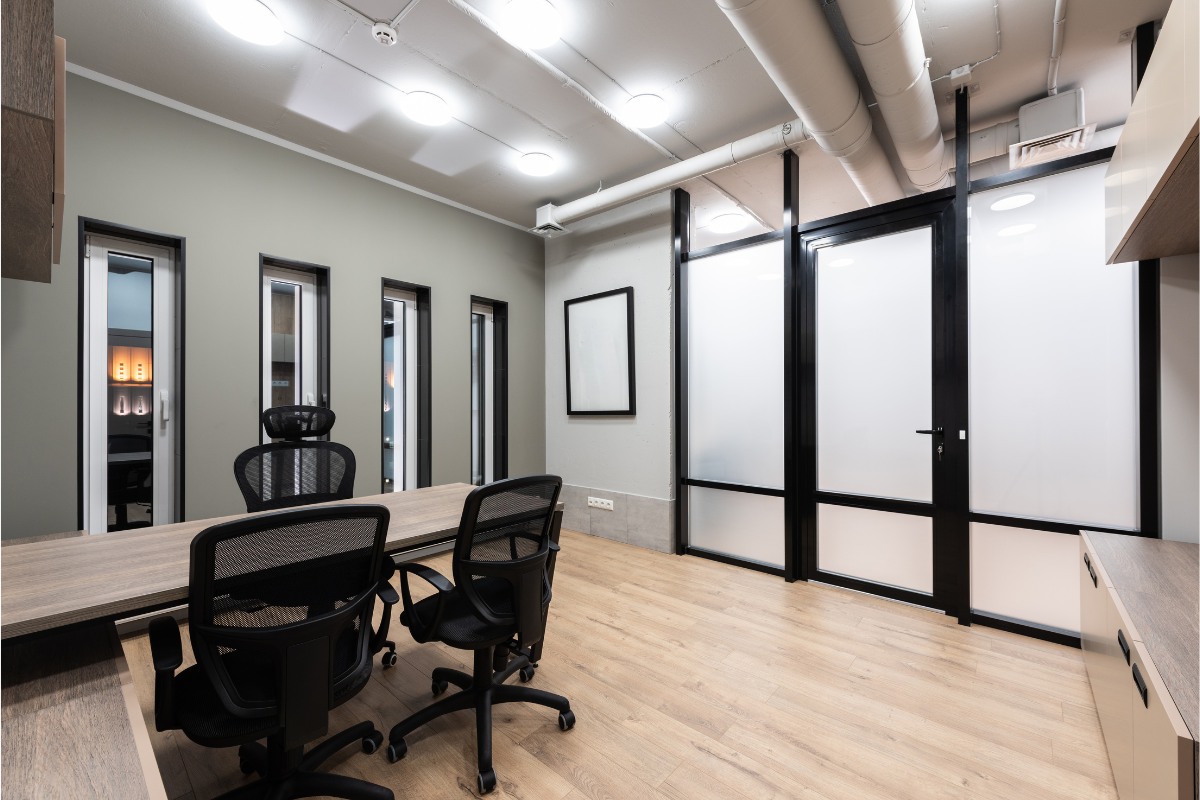
Lighting occupancy sensors are a common lighting solution, frequently employed as an energy-saving and cost-cutting measure in a wide variety of commercial and industrial workspaces. Motion sensors determine when a person has entered the room and instruct the light to turn on. After a set period during which the sensor detects no motion in the room, it commands the light to switch off, assuming the person has left the room.
Lighting occupancy sensors are ideal for work environments because they reduce energy usage and eliminate the need for employees to remember to turn off the lights. If you’re installing a lighting occupancy sensor in a facility, it’s important to remember that there are a number of things you can do to improve its performance and get the most out of this already energy-efficient fixture. Learn more about ensuring the correct operation and maximizing the performance of lighting occupancy sensors in our blog.
Lighting Occupancy Sensor Operation and Performance
- Ensure that the wiring that connects the sensor/power pack to the power/loads is correct. Incorrect wiring can reduce performance and/or present a safety hazard. It is advisable to consult the installation manual closely or seek professional assistance if uncertainties arise during the installation process.
- Ensure that the sensor is placed and oriented as it was in the original drawings. Deviations from the planned layout can significantly impact the sensor’s effectiveness. Additionally, consider environmental factors such as heat sources or air currents that might affect the sensor’s operation.
- Real-world installation may require a series of adjustments in order to fine-tune and calibrate the sensor’s operation. It’s crucial to test the sensor under various conditions to ensure it operates reliably under all expected circumstances. Consider environmental factors such as the placement of furniture or equipment that might obstruct the sensor’s field of view.
Time-Delay
The time-delay setting allows the operator to adjust how long the lights will stay on after the last instance of motion is detected. The usual recommended minimum delay is 15 minutes. This does several things.
First, it avoids on-off cycles that are too frequent, if occupants enter and leave the room on a regular basis. This prevents the occupants of the room from being distracted, and will also prolong the life of the bulb. It also prevents the lights from going off too soon if an occupant has entered the room but does not move after his or her entrance. Finally, it generates an acceptable compromise between energy savings and performance.
For different environments, adjusting the time-delay to suit the specific usage patterns can optimize energy savings without sacrificing comfort. For instance, in a rarely used storeroom, a shorter delay might be more appropriate, whereas in a busy office, a longer delay ensures that the lights remain on as needed. In environments such as libraries or study areas, where occupants may remain still for longer periods, considering a longer time-delay may be beneficial to avoid disruptions.
Motion Sensitivity
This setting allows for the sensor’s sensitivity to motion to be adjusted. The lower the sensitivity, the more sensitive the sensor will be to motion, meaning even small motions will turn on the lights. Higher sensitivity settings will require more distinct motions to activate the sensor. Following the installation of the sensor, there is usually a trial period during which the operator can work with the room’s occupants to fine-tune this setting to their satisfaction.
Maybe You Are Interested In
Adjusting the sensitivity is particularly important in areas with varying levels of activity; for example, in conference rooms, a higher sensitivity might be necessary to detect minimal movements during meetings. For areas with high traffic or those prone to small, incidental movements, adjusting the sensitivity to a lower setting can help in reducing false triggers and enhancing energy savings.
Get Inspired by Rayzeek Motion Sensor Portfolios.
Doesn't find what you want? Don't worry. There are always alternate ways to solve your problems. Maybe one of our portfolios can help.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of occupancy sensors. Periodic checks should be conducted to ensure that sensors are free from dust, debris, and any obstructions that could impair functionality. Common issues such as flickering lights or unresponsive sensors often indicate a need for recalibration or, in some cases, replacement of components. Additionally, it’s beneficial to review sensor settings annually to confirm that they remain aligned with the current usage patterns of the space.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Implementing lighting occupancy sensors can lead to significant cost savings over traditional lighting systems. By reducing the amount of energy consumed and minimizing the wear and tear on lighting fixtures, these sensors not only lower energy bills but also decrease maintenance costs.
An analysis of energy usage before and after installation often shows a reduction in energy consumption by up to 30-50%, depending on the nature of the workspace and the accuracy of the sensor settings. These savings not only cover the initial investment in the sensors but also contribute to a lower environmental impact over time.
Compatibility with Different Lighting Types
Occupancy sensors are versatile and can be integrated with various types of lighting technologies, including LED, fluorescent, and incandescent lighting. However, it is crucial to ensure compatibility between the sensor and the lighting type to avoid issues such as reduced lifespan of bulbs or improper functioning of the sensor.
Looking For Motion-Activated Energy-Saving Solutions?
Contact us for complete PIR motion sensors, motion-activated energy-saving products, motion sensor switches, and Occupancy/Vacancy commercial solutions.
Also, lighting occupancy sensors can be effectively integrated with other building management systems to create a smart, responsive environment. For example, connecting occupancy sensors with HVAC systems can further enhance energy efficiency by coordinating lighting and temperature based on actual room usage. This integration not only optimizes energy use but also improves the overall comfort and productivity of the occupants.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
In many regions, there are specific regulations and standards that govern the installation of electrical devices, including occupancy sensors. Familiarity with these regulations is essential to ensure compliance and avoid legal issues. Additionally, adherence to standards can often enhance the system’s efficiency and safety.
Understanding and addressing these aspects can help facilities maximize the benefits of lighting occupancy sensors, leading to a more energy-efficient and cost-effective operation.